但在这里有一点需要注意,我们平时有可能在类名中会使用分隔线,比如:
<style module>
.btn-lg {
border: 1px solid red;
padding: 10px 30px;
}
</style>
如果通过 $style 调用该类名时要是写成 $style.btn-lg ,这样写是一个不合法的JavaScript变量名。此时在编译的时候,会报一个错话信息:
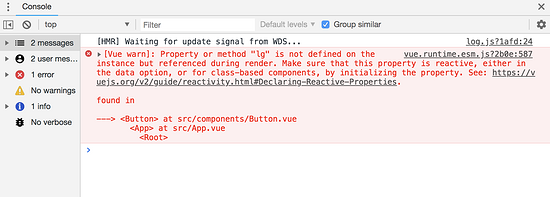
按钮的样式也不会生效。如果要生效,我们需要通过下面这样的方式来写:
<template>
<button :class="$style['btn-lg']">{{msg}}</button>
</template>
编译出来的结果如下:
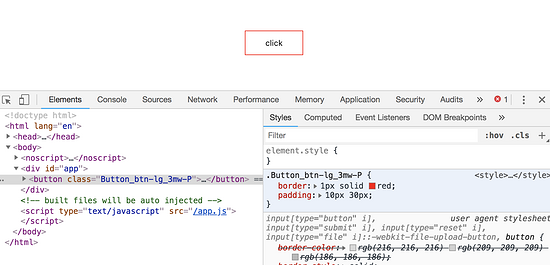
除了$style.btn-lg这种方式会报错之外,写在驼峰($style.btnLg)的也会报错。
上面说的 module 属性会经由Vue-loader编译后,在我们的 component 产生一个叫 $style 的隐藏的 computed 属性。也就是说,我们甚至可以在Vue生命周期的 created 钩子中取得由CSS Modules生成的 class 类名:
<script>
export default {
created () {
console.log(this.$style['btn-lg'])
}
}
</script>
在浏览器的 console 中可以看到 modules 编译出来对应的类名:
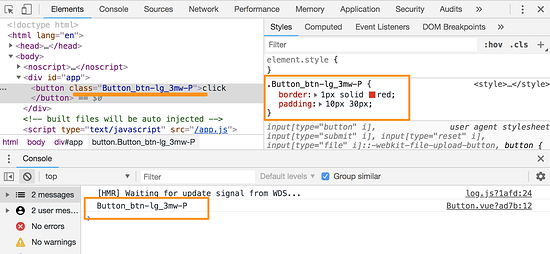
利用这样的特性,在 <template> 也可以这样写:
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<div id="app">
<Button msg="Default Button" />
<Button :class="{[$style['btn-lg']]: isLg}" msg="Larger Button" />
<Button :class="{[$style['btn-sm']]: isSm}" msg="Smaller Button" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Button from './components/Button'
export default {
name: 'app',
components: {
Button
},
data () {
return {
isLg: true,
isSm: false
}
}
}
</script>
<style module>
.btn-lg {
padding: 15px 30px;
}
.btn-sm {
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
内容版权声明:除非注明,否则皆为本站原创文章。
