最近正在看spring官网,看Spring IOC的时候看Spring容器扩展点的时候发现了BeanPostProcessor 这个接口。下面是官方对它的详细描述:
BeanPostProcessor接口定义了回调方法,您可以实现提供自己的(或覆盖容器的默认)实例化逻辑,依赖性解析逻辑,等等。如果你想实现一些自定义逻辑Spring容器实例化完成后,配置和初始化一个bean,您可以插入一个或多个BeanPostProcessor实现。
您可以配置多个BeanPostProcessor实例,您可以控制的顺序执行这些BeanPostProcessors通过设置属性。你可以设置这个属性只有BeanPostProcessor实现命令接口;如果你写自己的BeanPostProcessor你也应该考虑实现theOrdered接口。详情,请咨询BeanPostProcessor的Javadoc和命令接口。
BeanPostProcessor有两个方法postProcessBeforeInitialization,postProcessAfterInitialization.如果一个对象实现了这个接口,那么就会在容器初始化init方法之前(就像InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()和其它公开的init方法)或在Spring bean初始化之后执行回调。
实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类由容器是特殊而区别对待。所有BeanPostProcessors和他们在启动时直接引用实例化bean,作为特殊的ApplicationContext的启动阶段。接下来,所有BeanPostProcessorsare注册分类的方式,适用于所有进一步bean容器。因为实现AOP auto-proxying aBeanPostProcessor本身,无论是BeanPostProcessors还是beas他们有资格获得auto-proxying直接引用,因此没有方面编织进去。
实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类由容器是特殊而区别对待。所有BeanPostProcessors和他们在启动时直接引用实例化bean,作为特殊的ApplicationContext的启动阶段。接下来,所有BeanPostProcessorsare注册分类的方式,适用于所有进一步bean容器。因为实现AOP auto-proxying aBeanPostProcessor本身,无论是BeanPostProcessors还是beas他们有资格获得auto-proxying直接引用,因此没有方面编织进去。
使用回调接口或注释与自定义实现BeanPostProcessor是一种常见的扩展SpringIoC容器。RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是Spring的一个例子 —— 一个实现BeanPostProcessor附带的Spring分布,确保JavaBean属性bean上标有一个(任意)注释(配置)会依赖注入值。
你说我一看到上面的AOP这个Spring两大特性之一我心里面都有一点小激动。后面他再来个Spring的Annotation一般也是用这个接口实现的。这下就忍不住了想去看一看RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个类到底干了什么。直接上源码
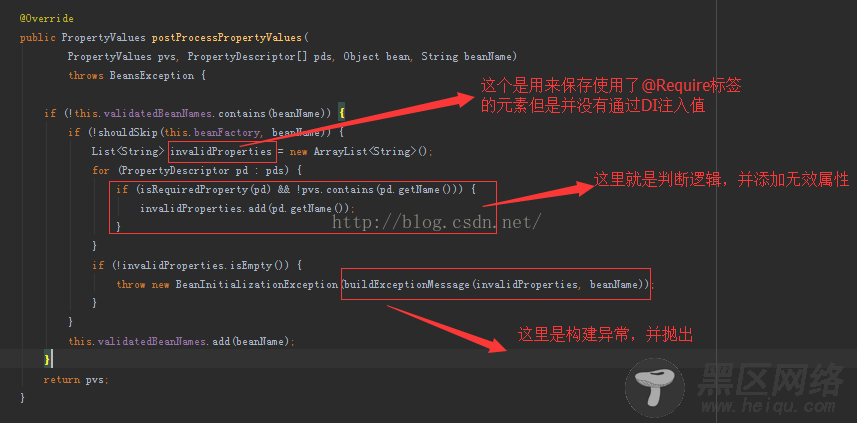
Spring Annotation Support /* * Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition; import org.springframework.core.Conventions; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor} implementation * that enforces required JavaBean properties to have been configured. * 强制检测JavaBean必须的properties是否已经被配置 * Required bean properties are detected through a Java 5 annotation: * 必须的bean属性通过Java 5中的annotation自动检测到 * by default, Spring's {@link Required} annotation. * * <p>The motivation for the existence of this BeanPostProcessor is to allow * BeanPostProcessor存在的意义是允许 * developers to annotate the setter properties of their own classes with an * arbitrary JDK 1.5 annotation to indicate that the container must check * for the configuration of a dependency injected value. This neatly pushes * 开发人员注释setter属性与一个他们自己的类任意的JDK 1.5注释表明容器必须检查依赖注入的配置值。 * responsibility for such checking onto the container (where it arguably belongs), * 这样就巧妙的把check的责任给了Spring容器(它应该就属于的) * and obviates the need (<b>in part</b>) for a developer to code a method that * simply checks that all required properties have actually been set. * 这样也就排除了开发人员需要编写一个简单的方法用来检测那么必须的properties是否已经设置了值 * <p>Please note that an 'init' method may still need to implemented (and may * still be desirable), because all that this class does is enforce that a * 请注意初始化方法还是必须要实现的(并且仍然是可取的) * 'required' property has actually been configured with a value. It does * 因为所有这个Class强制执行的是'required'属性是否已经被配置了值 * <b>not</b> check anything else... In particular, it does not check that a * 它并不会check其实的事,特别的是,它不会check这个配置的值是不是null值 * configured value is not {@code null}. * * <p>Note: A default RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor will be registered * by the "context:annotation-config" and "context:component-scan" XML tags. * 当你使用了"context:annotation-config"或者"context:component-scan"XML标签就会默认注册RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor * Remove or turn off the default annotation configuration there if you intend * to specify a custom RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bean definition. * 你如果打算指定一个自定义的RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的bean实现可以移除或者关闭默认的annotation配置 * * @author Rob Harrop * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 2.0 * @see #setRequiredAnnotationType * @see Required */ public class RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, BeanFactoryAware { /** * Bean definition attribute that may indicate whether a given bean is supposed * to be skipped when performing this post-processor's required property check. * 这个bean定义的属性表明当执行post-processor(后处理程序)这个check提供的bean的必须的属性 * @see #shouldSkip */ public static final String SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE = Conventions.getQualifiedAttributeName(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class, "skipRequiredCheck"); private Class<? extends Annotation> requiredAnnotationType = Required.class; private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1; private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory; /** * Cache for validated bean names, skipping re-validation for the same bean * 缓存已经确认过的bean名称,跳过后续同样的bean */ private final Set<String> validatedBeanNames = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(64)); /** * Set the 'required' annotation type, to be used on bean property * setter methods. * 设置所需的注释类型,使用bean属性setter方法 * <p>The default required annotation type is the Spring-provided * {@link Required} annotation. * 这个默认的required annotation类型是Spring提供的annotation * <p>This setter property exists so that developers can provide their own * (non-Spring-specific) annotation type to indicate that a property value * is required. * 这里设置这个property是为了开发者能够提供自己定义的annotaion类型用来表明这个属性值是必须的 */ public void setRequiredAnnotationType(Class<? extends Annotation> requiredAnnotationType) { Assert.notNull(requiredAnnotationType, "'requiredAnnotationType' must not be null"); this.requiredAnnotationType = requiredAnnotationType; } /** * Return the 'required' annotation type. */ protected Class<? extends Annotation> getRequiredAnnotationType() { return this.requiredAnnotationType; } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) { if (beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { this.beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory; } } public void setOrder(int order) { this.order = order; } @Override public int getOrder() { return this.order; } @Override public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { } @Override public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues( PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // 利用缓存确定是否这个bean被validated if (!this.validatedBeanNames.contains(beanName)) { // 不跳过 if (!shouldSkip(this.beanFactory, beanName)) { List<String> invalidProperties = new ArrayList<String>(); for (PropertyDescriptor pd : pds) { // 如果被标记为了required 且 这个属性没有属性值(或其他处理条目) if (isRequiredProperty(pd) && !pvs.contains(pd.getName())) { // 增加这个属性 invalidProperties.add(pd.getName()); } } // <span>如果无效的properties不为空。抛出异常</span> if (!invalidProperties.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanInitializationException(buildExceptionMessage(invalidProperties, beanName)); } } // 把需要验证的bean名称添加进去 this.validatedBeanNames.add(beanName); } return pvs; } /** * Check whether the given bean definition is not subject to the annotation-based * required property check as performed by this post-processor. * 通过post-processor(后处理程序)检测这个被给予的定义的bean是否受注释为基础的check必须的property的管束 * <p>The default implementations check for the presence of the * {@link #SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE} attribute in the bean definition, if any. * 这个默认的实现check存在SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE这个属性的定义的bean * It also suggests skipping in case of a bean definition with a "factory-bean" * reference set, assuming that instance-based factories pre-populate the bean. * 它同样也建议跳过如果这个bean定义了"factory-bean"引用,假设那个基于实例的factories预先配置了bean * @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to check against * @param beanName the name of the bean to check against * @return {@code true} to skip the bean; {@code false} to process it * 如果返回 true跳过这个bean,返回false就处理它 */ protected boolean shouldSkip(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) { // 如果这个beanFacotry为空或者这个bean工厂不包含一个给定名称的bean定义。返回false if (beanFactory == null || !beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { return false; } BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName); // 判断这个bean的工厂beanName,如果不为null,返回true if (beanDefinition.getFactoryBeanName() != null) { return true; } Object value = beanDefinition.getAttribute(SKIP_REQUIRED_CHECK_ATTRIBUTE); return (value != null && (Boolean.TRUE.equals(value) || Boolean.valueOf(value.toString()))); } /** * Is the supplied property required to have a value (that is, to be dependency-injected)? * 是否这个提供的必须的propery是否有一个值(这个是被依赖注入)? * <p>This implementation looks for the existence of a * {@link #setRequiredAnnotationType "required" annotation} * on the supplied {@link PropertyDescriptor property}. * 这个实现是为了找到提供的ProertyDescriptor是提供了"required"注解 * @param propertyDescriptor the target PropertyDescriptor (never {@code null}) * @return {@code true} if the supplied property has been marked as being required; * 返回true,如果提供的property已经被标记为必须的</span> * {@code false} if not, or if the supplied property does not have a setter method * 返回false,如果没有标记为必须的或者提供的property没有一个setter方法 */ protected boolean isRequiredProperty(PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor) { Method setter = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod(); return (setter != null && AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(setter, getRequiredAnnotationType()) != null); } /** * Build an exception message for the given list of invalid properties. * 使用所给的异常properties来构建异常信息 * @param invalidProperties the list of names of invalid properties * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the exception message */ private String buildExceptionMessage(List<String> invalidProperties, String beanName) { int size = invalidProperties.size(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(size == 1 ? "Property" : "Properties"); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { String propertyName = invalidProperties.get(i); if (i > 0) { if (i == (size - 1)) { sb.append(" and"); } else { sb.append(","); } } sb.append(" '").append(propertyName).append("'"); } sb.append(size == 1 ? " is" : " are"); sb.append(" required for bean '").append(beanName).append("'"); return sb.toString(); } }
在上面的代码中所示。我们可以得出以下结论: