ARGV[2] 是:“id + ":" + threadId”
如果同一个机器同一个线程再次来请求,这里就会是1,然后执行hincrby, hset设置的value+1 变成了2,然后继续设置过期时间。
同理,一个线程重入后,解锁时value - 1
Redisson watchDog原理如果一个场景:现在有A,B在执行业务,A加了分布式锁,但是生产环境是各种变化的,如果万一A锁超时了,但是A的业务还在跑。而这时由于A锁超时释放,B拿到锁,B执行业务逻辑。这样分布式锁就失去了意义?
所以Redisson 引入了watch dog的概念,当A获取到锁执行后,如果锁没过期,有个后台线程会自动延长锁的过期时间,防止因为业务没有执行完而锁过期的情况。
我们接着来看看具体实现:
1private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {2 if (leaseTime != -1) {
3 return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
4 }
5 RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
6 ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
7 @Override
8 public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
9 if (!future.isSuccess()) {
10 return;
11 }
12
13 Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();
14 // lock acquired
15 if (ttlRemaining == null) {
16 scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
17 }
18 }
19 });
20 return ttlRemainingFuture;
21}
当我们tryLockInnerAsync执行完之后,会添加一个监听器,看看监听器中的具体实现:
1protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {2 return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
3 "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
4 "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
5 "return 1; " +
6 "end; " +
7 "return 0;",
8 Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()),
9 internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
10}
这里面调度任务每隔10s钟执行一次,lua脚本中是续约过期时间,使得当前线程持有的锁不会因为过期时间到了而失效
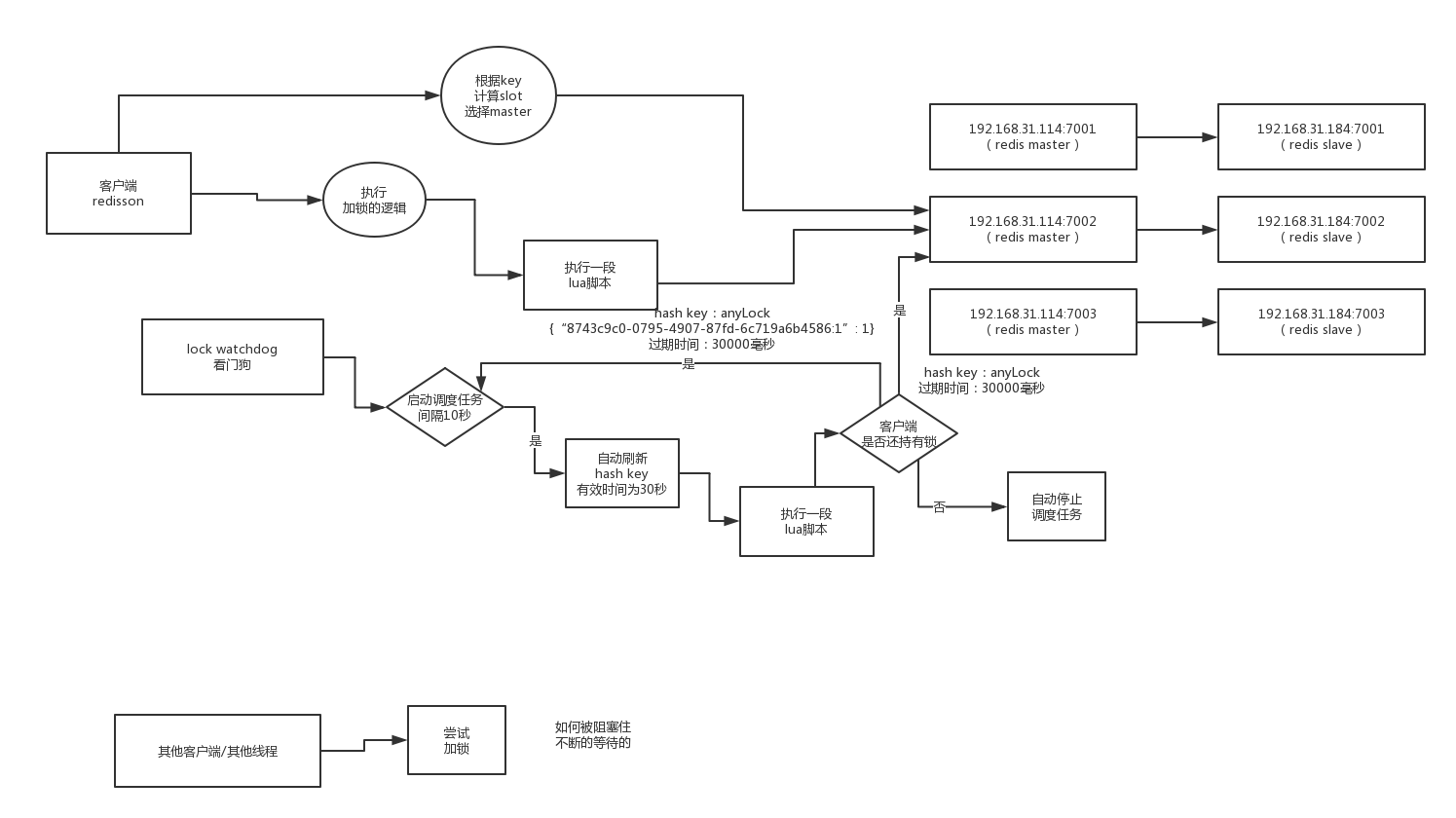
还是看上面执行加锁的lua脚本,最后会执行到:
1"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",返回锁还有多久时间过期,我们继续接着看代码:
1@Override2public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
3 long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
4 Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
5 // 返回ttl说明加锁成功,不为空则是加锁失败
6 if (ttl == null) {
7 return;
8 }
9
10 RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
11 commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
12
13 try {
14 // 死循环去尝试获取锁
15 while (true) {
16 // 再次尝试加锁
17 ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
18 // 如果ttl=null说明抢占锁成功
19 if (ttl == null) {
20 break;
21 }
22
23 // ttl 大于0,抢占锁失败,这个里面涉及到Semaphore,后续会讲解
24 if (ttl >= 0) {
25 getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
26 } else {
27 getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
28 }
29 }
30 } finally {
31 unsubscribe(future, threadId);
32 }
33}
Redisson锁释放原理

