我们都知道,只要合理正确使用PDO,可以基本上防止SQL注入的产生,本文主要回答以下两个问题:
为什么要使用PDO而不是mysql_connect?
为何PDO能防注入?
使用PDO防注入的时候应该特别注意什么?
一、为何要优先使用PDO?
PHP手册上说得很清楚:
Prepared statements and stored procedures
Many of the more mature databases support the concept of prepared statements. What are they? They can be thought of as a kind of compiled template for the SQL that an application wants to run, that can be customized using variable parameters. Prepared statements offer two major benefits:
The query only needs to be parsed (or prepared) once, but can be executed multiple times with the same or different parameters. When the query is prepared, the database will analyze, compile and optimize its plan for executing the query. For complex queries this process can take up enough time that it will noticeably slow down an application if there is a need to repeat the same query many times with different parameters. By using a prepared statement the application avoids repeating the analyze/compile/optimize cycle. This means that prepared statements use fewer resources and thus run faster.
The parameters to prepared statements don't need to be quoted; the driver automatically handles this. If an application exclusively uses prepared statements, the developer can be sure that no SQL injection will occur (however, if other portions of the query are being built up with unescaped input, SQL injection is still possible).
即使用PDO的prepare方式,主要是提高相同SQL模板查询性能、阻止SQL注入
同时,PHP手册中给出了警告信息
Prior to PHP 5.3.6, this element was silently ignored. The same behaviour can be partly replicated with the PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND driver option, as the following example shows.
Warning
The method in the below example can only be used with character sets that share the same lower 7 bit representation as ASCII, such as ISO-8859-1 and UTF-8. Users using character sets that have different representations (such as UTF-16 or Big5) must use the charset option provided in PHP 5.3.6 and later versions.
意思是说,在PHP 5.3.6及以前版本中,并不支持在DSN中的charset定义,而应该使用PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND设置初始SQL, 即我们常用的 set names gbk指令。
我看到一些程序,还在尝试使用addslashes达到防注入的目的,殊不知这样其实问题更多, 详情请看https://www.jb51.net/article/49205.htm
还有一些做法:在执行数据库查询前,将SQL中的select, union, ....之类的关键词清理掉。这种做法显然是非常错误的处理方式,如果提交的正文中确实包含 the students's union , 替换后将篡改本来的内容,滥杀无辜,不可取。
二、为何PDO能防SQL注入?
请先看以下PHP代码:
复制代码 代码如下:
<?php
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=192.168.0.1;dbname=test;charset=utf8","root");
$st = $pdo->prepare("select * from info where id =? and name = ?");
$id = 21;
$name = 'zhangsan';
$st->bindParam(1,$id);
$st->bindParam(2,$name);
$st->execute();
$st->fetchAll();
?>
环境如下:
PHP 5.4.7
Mysql 协议版本 10
MySQL Server 5.5.27
为了彻底搞清楚php与mysql server通讯的细节,我特别使用了wireshark抓包进行研究之,安装wireshak之后,我们设置过滤条件为tcp.port==3306, 如下图:

如此只显示与mysql 3306端口的通信数据,避免不必要的干扰。
特别要注意的是wireshak基于wincap驱动,不支持本地环回接口的侦听(即使用php连接本地mysql的方法是无法侦听的),请连接其它机器(桥接网络的虚拟机也可)的MySQL进行测试。
然后运行我们的PHP程序,侦听结果如下,我们发现,PHP只是简单地将SQL直接发送给MySQL Server :
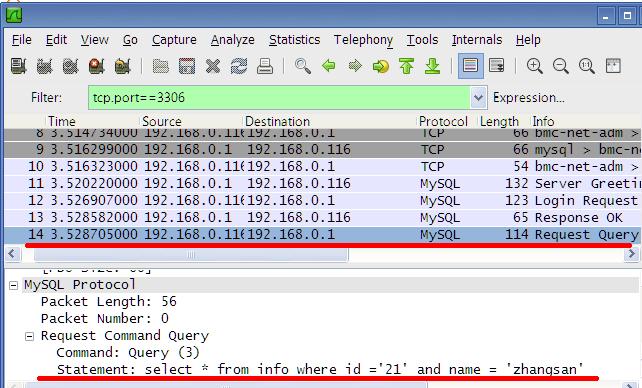
其实,这与我们平时使用mysql_real_escape_string将字符串进行转义,再拼接成SQL语句没有差别(只是由PDO本地驱动完成转义的),显然这种情况下还是有可能造成SQL注入的,也就是说在php本地调用pdo prepare中的mysql_real_escape_string来操作query,使用的是本地单字节字符集,而我们传递多字节编码的变量时,有可能还是会造成SQL注入漏洞(php 5.3.6以前版本的问题之一,这也就解释了为何在使用PDO时,建议升级到php 5.3.6+,并在DSN字符串中指定charset的原因。
针对php 5.3.6以前版本,以下代码仍然可能造成SQL注入问题:
复制代码 代码如下:
