不久前 Fedora 21 发布了,版本有三个,其中有一个服务器版本,原文提示采用的就是 Server 服务器版本,先看看 LAMP 是 Linux、Apache、MySQL/MariaDB、PHP 的简称。
本教程采用的实例域名为 server1.example.com,IP 地址为 192.168.0.100,实际上你安装的时候有所不同,请作相应修改。
1、先安装数据库MySQL/MariaDB 5。
MariaDB 安装命令:
yum install mariadb mariadb-server
为 MariaDB 创建开机自启动:
systemctl enable mariadb.service
启动 mysql 服务:
systemctl start mariadb.service
mysql_secure_installation
设置超级root用户密码,按照提示操作:
[root@server1 ~]# mysql_secure_installation
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation: line 379: find_mysql_client: command not found
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we’ll need the current
password for the root user. If you’ve just installed MariaDB, and
you haven’t set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): <– ENTER
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] <– ENTER
New password: <– 输入密码
Re-enter new password: <– 再输入一次密码
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
… Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] <– ENTER
… Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from ‘localhost’. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] <– ENTER
… Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named ‘test’ that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] <– ENTER
– Dropping test database…
… Success!
– Removing privileges on test database…
… Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] <– ENTER
… Success!
Cleaning up…
All done! If you’ve completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
[root@server1 ~]#
2、安装Apache2
yum install httpd
设置随系统自启动:
systemctl enable httpd.service
启动服务:
systemctl start httpd.service
接下来我们需要添加Apache服务覆盖在防火墙命令如下:
firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
firewall-cmd --reload
好了,输入IP地址:,看看 apache 运行情况:
Fedora 系统 Apache 默认根目录 /var/www/html,配置文件目录 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf,其他配置文件目录 /etc/httpd/conf.d/ directory。
3、安装PHP5
安装命令:
yum install php
重启 apache 命令:
systemctl restart httpd.service
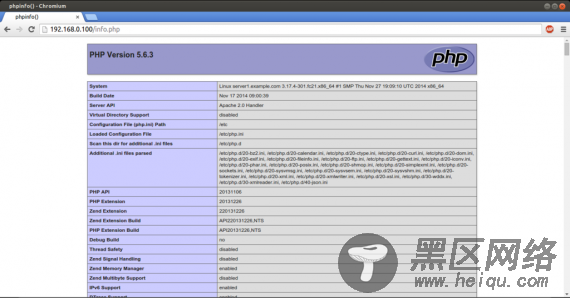
4、测试 PHP5 获取 PHP5 安装情况:
在根目录下创建一个探针文件:
nano /var/www/html/info.php
添加文件内容:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>然后访问探针文件: