在vue实例中,通过$mount()实现实例的挂载,下面来分析一下$mount()函数都实现了什么功能。
$mount函数执行位置
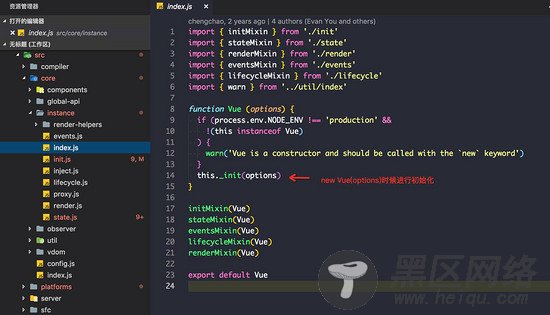
_init这个私有方法是在执行initMixin时候绑定到Vue原型上的。
$mount函数是如如何把组件挂在到指定元素
$mount函数定义位置
$mount函数定义位置有两个:
第一个是在src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js
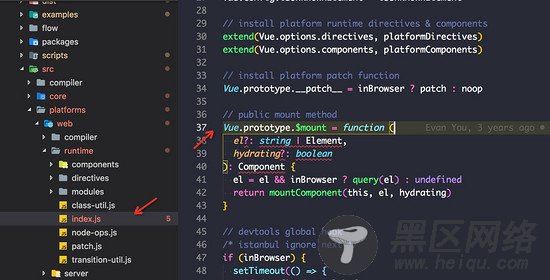
这里的$mount是一个public mount method。之所以这么说是因为Vue有很多构建版本, 有些版本会依赖此方法进行有些功能定制, 后续会解释。
// public mount method // el: 可以是一个字符串或者Dom元素 // hydrating 是Virtual DOM 的补丁算法参数 Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { // 判断el, 以及宿主环境, 然后通过工具函数query重写el。 el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined // 执行真正的挂载并返回 return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) }
src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js 文件是运行时版 Vue 的入口文件,所以这个方法是运行时版本Vue执行的$mount。
关于Vue不同构建版本可以看 。
关于这个作者封装的工具函数query也可以学习下:
/** * Query an element selector if it's not an element already. */ export function query (el: string | Element): Element { if (typeof el === 'string') { const selected = document.querySelector(el) if (!selected) { // 开发环境下给出错误提示 process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( 'Cannot find element: ' + el ) // 没有找到的情况下容错处理 return document.createElement('div') } return selected } else { return el } }
第二个定义 $mount 函数的地方是src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 文件,这个文件是完整版Vue(运行时+编译器)的入口文件。
关于运行时与编译器不清楚的童鞋可以看官网 。
// 缓存运行时候定义的公共$mount方法 const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { // 通过query方法重写el(挂载点: 组件挂载的占位符) el = el && query(el) /* istanbul ignore if */ // 提示不能把body/html作为挂载点, 开发环境下给出错误提示 // 因为挂载点是会被组件模板自身替换点, 显然body/html不能被替换 if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.` ) return this } // $options是在new Vue(options)时候_init方法内执行. // $options可以访问到options的所有属性如data, filter, components, directives等 const options = this.$options // resolve template/el and convert to render function // 如果包含render函数则执行跳出,直接执行运行时版本的$mount方法 if (!options.render) { // 没有render函数时候优先考虑template属性 let template = options.template if (template) { // template存在且template的类型是字符串 if (typeof template === 'string') { if (template.charAt(0) === '#') { // template是ID template = idToTemplate(template) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) { warn( `Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this ) } } } else if (template.nodeType) { // template 的类型是元素节点,则使用该元素的 innerHTML 作为模板 template = template.innerHTML } else { // 若 template既不是字符串又不是元素节点,那么在开发环境会提示开发者传递的 template 选项无效 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn('invalid template option:' + template, this) } return this } } else if (el) { // 如果template选项不存在,那么使用el元素的outerHTML 作为模板内容 template = getOuterHTML(el) } // template: 存储着最终用来生成渲染函数的字符串 if (template) { /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile') } // 获取转换后的render函数与staticRenderFns,并挂在$options上 const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, { outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', shouldDecodeNewlines, shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref, delimiters: options.delimiters, comments: options.comments }, this) options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns /* istanbul ignore if */ // 用来统计编译器性能, config是全局配置对象 if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile end') measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end') } } } // 调用之前说的公共mount方法 // 重写$mount方法是为了添加模板编译的功能 return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) }
关于idToTemplate方法: 通过query获取该ID获取DOM并把该元素的innerHTML 作为模板
const idToTemplate = cached(id => { const el = query(id) return el && el.innerHTML })
getOuterHTML方法:
