简单的说,就是插入排序总共需要排序N-1趟,从index为1开始,讲该位置上的元素与之前的元素比较,放入合适的位置,这样循环下来之后,即为有序数组。
代码实现:
public class InsertionSort extends SortBase {
@Override
public Integer[] sort(Integer[] a) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
print("init",a);
Integer temp = 0;
for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++) {
//只能从当前索引往前循环,因为索引前的数组皆为有序的,索引只要确定当前索引的数据的为止即可
for(int j=i;j>0 && a[j] < a[j-1];j--) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j-1];
a[j-1] = temp;
}
print(i +"",a);
}
print("result",a);
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = {2,1,5,9,0,6,8,7,3};
(new InsertionSort()).sort(a);
}
}
运行结果:
init: [2 ,1 ,5 ,9 ,0 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
1: [1 ,2 ,5 ,9 ,0 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
2: [1 ,2 ,5 ,9 ,0 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
3: [1 ,2 ,5 ,9 ,0 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
4: [0 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,9 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
5: [0 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,6 ,9 ,8 ,7 ,3]
6: [0 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,9 ,7 ,3]
7: [0 ,1 ,2 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,3]
8: [0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9]
result: [0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9]
效率:如果目标是把n个元素的序列升序排列,那么采用插入排序存在最好情况和最坏情况。最好情况就是,序列已经是升序排列了,在这种情况下,需要进行的比较操作需(n-1)次即可。最坏情况就是,序列是降序排列,那么此时需要进行的比较共有n(n-1)/2次。插入排序的赋值操作是比较操作的次数加上 (n-1)次。平均来说插入排序算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2)
四、希尔排序
把记录按步长 gap 分组,对每组记录采用直接插入排序方法进行排序。
随着步长逐渐减小,所分成的组包含的记录越来越多,当步长的值减小到 1 时,整个数据合成为一组,构成一组有序记录,则完成排序。
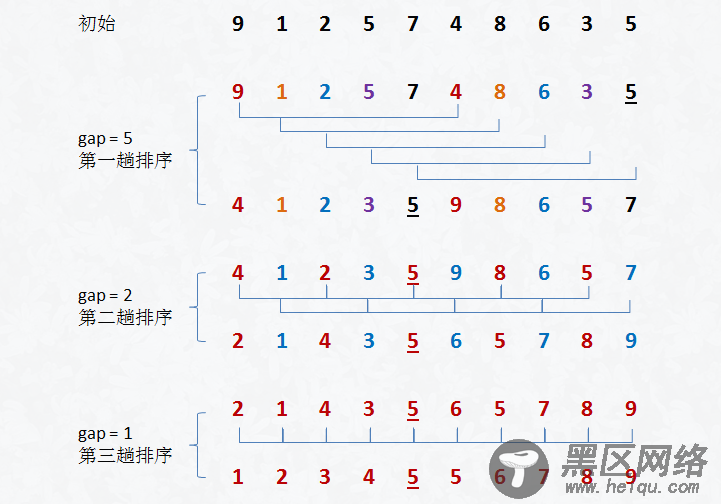
实现代码:
public class ShellSort extends SortBase {
@Override
public Integer[] sort(Integer[] a) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
print("init",a);
Integer h = a.length;
Integer temp = 0;
while(h >= 1) {
for(int i=h;i<a.length;i++) {
for(int j=i;j>=h && a[j] < a[j-h];j -= h) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j-h];
a[j-h] = temp;
}
}
h /= 9;
}
print("result",a);
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = {2,1,5,9,0,6,8,7,3};
(new ShellSort()).sort(a);
}
}
运行结果:
init: [2 ,1 ,5 ,9 ,0 ,6 ,8 ,7 ,3]
1: [0 ,1 ,5 ,7 ,2 ,6 ,8 ,9 ,3]
2: [0 ,1 ,2 ,6 ,3 ,7 ,5 ,9 ,8]
3: [0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9]
result: [0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9]

