在C++中引入thread头文件可以很容易地实现多线程。
#include <thread>引入头文件后,我们需要将每一个线程写成函数的形式。如示例中的inc()与dec()函数。
void inc() { int time = TIME; while(time--) { num++; } } void dec() { int time = TIME; while(time--) { num--; } }之后我们通过线程类的初始化就可以很容易地创建并运行线程。
std::thread t1(inc); std::thread t2(dec);注意:在主线程中,我们需要用thread.join() 来阻塞等待结束每一个线程。否则主线程提前结束程序会出错。
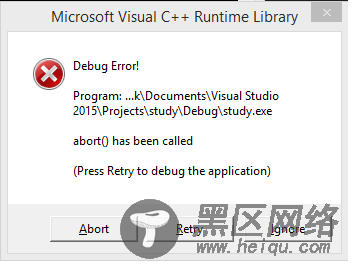
下面是这个示例中完整的代码,代码中模拟了线程对临界资源的操作。不同的运行,num的值可能会不一样。这在我们的实际的编程中要注意。
#include <thread> #include <iostream> #define TIME 1000000 int num = 0; void inc() { int time = TIME; while(time--) { num++; } } void dec() { int time = TIME; while(time--) { num--; } } int main() { std::thread t1(inc); std::thread t2(dec); std::cout << "thread begin" << std::endl; t1.join(); t2.join(); std::cout << "The num is : " << num << std::endl; return 0; }
