Python中,list这种数据结构很常用到,如果两个或者多个list结构相同,内容类型相同,我们通常会将两个或者多个list合并成一个,这样我们再循环遍历的时候就可以一次性处理掉了。所以如何将两个或者多个list合并成一个就是我们接下来要讲的内容。
示例效果:
[[1,2],[3,4,5],[0,4]] 会成为 [[1,2],[0,3,4,5]
[[1],[1,2],[0,2]] 会成为 [[0,1,2]]
[[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]] 会成为 [[1,2,3,4]]
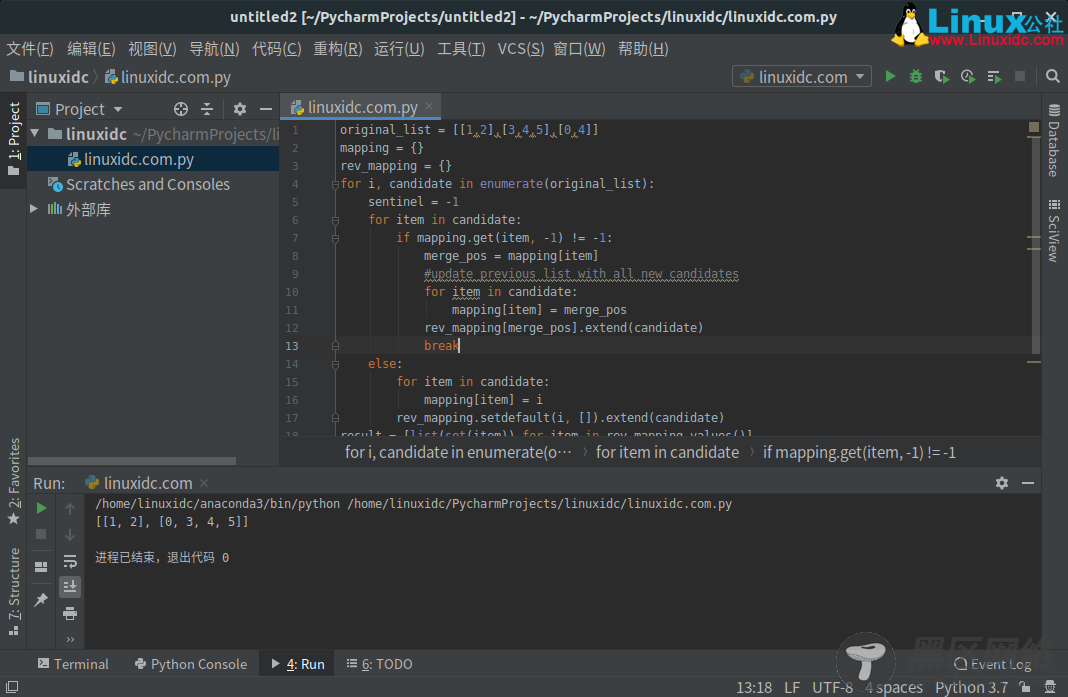
1、使用itertools实现
from itertools import combinations def bfs(graph, start): visited, queue = set(), [start] while queue: vertex = queue.pop(0) if vertex not in visited: visited.add(vertex) queue.extend(graph[vertex] - visited) return visited def connected_components(G): seen = set() for v in G: if v not in seen: c = set(bfs(G, v)) yield c seen.update(c) def graph(edge_list): result = {} for source, target in edge_list: result.setdefault(source, set()).add(target) result.setdefault(target, set()).add(source) return result def concat(l): edges = [] s = list(map(set, l)) for i, j in combinations(range(len(s)), r=2): if s[i].intersection(s[j]): edges.append((i, j)) G = graph(edges) result = [] unassigned = list(range(len(s))) for component in connected_components(G): union = set().union(*(s[i] for i in component)) result.append(sorted(union)) unassigned = [i for i in unassigned if i not in component] result.extend(map(sorted, (s[i] for i in unassigned))) return result print(concat([[1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [0, 4]])) print(concat([[1], [1, 2], [0, 2]])) print(concat([[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]]))
输出:
[[0, 3, 4, 5], [1, 2]]
[[0, 1, 2]]
[[1, 2, 3, 4]]
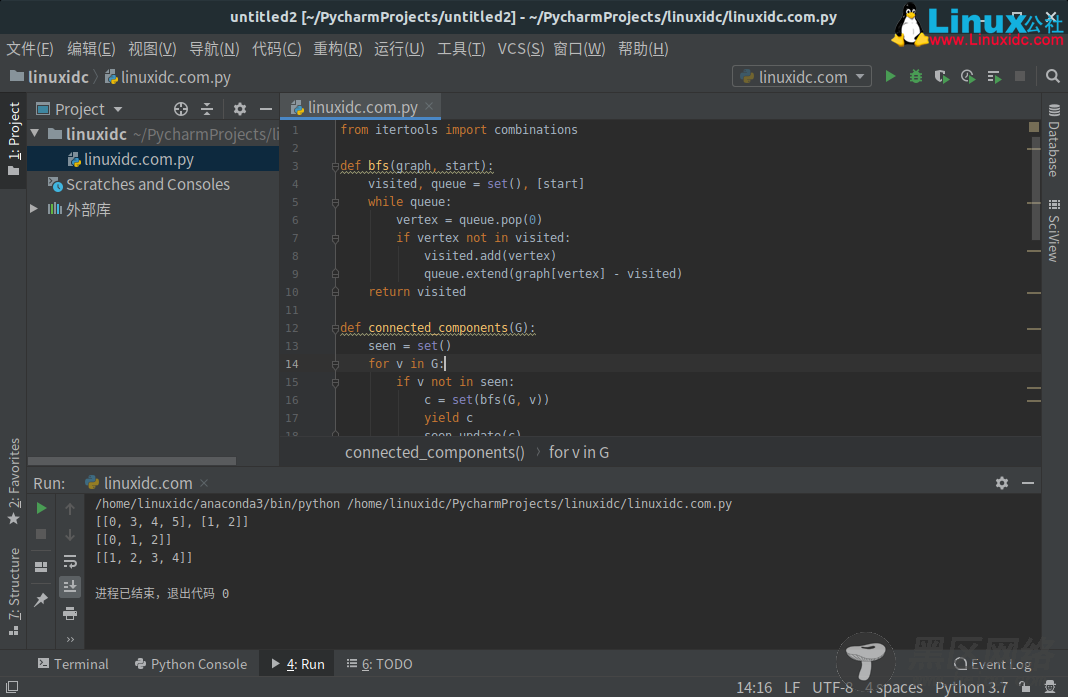
2、迭代方法实现
original_list = [[1,2],[3,4,5],[0,4]] mapping = {} rev_mapping = {} for i, candidate in enumerate(original_list): sentinel = -1 for item in candidate: if mapping.get(item, -1) != -1: merge_pos = mapping[item] #update previous list with all new candidates for item in candidate: mapping[item] = merge_pos rev_mapping[merge_pos].extend(candidate) break else: for item in candidate: mapping[item] = i rev_mapping.setdefault(i, []).extend(candidate) result = [list(set(item)) for item in rev_mapping.values()] print(result)
输出:
[[1, 2], [0, 3, 4, 5]]