// app.js // set the dimensions and margins of the graph const margin = { top: 20, right: 20, bottom: 30, left: 40 }; const width = 960 - margin.left - margin.right; const height = 500 - margin.top - margin.bottom; // set the ranges for the graph const x = d3 .scaleBand() .range([0, width]) .padding(0.1); const y = d3.scaleLinear().range([height, 0]); // append the container for the graph to the page const container = d3 .select('body') .append('div') .attr('class', 'container'); container.append('h1').text('Who will win the 2018/19 Premier League Season?'); // append the svg object to the body of the page // append a 'group' element to 'svg' // moves the 'group' element to the top left margin const svg = container .append('svg') .attr('width', width + margin.left + margin.right) .attr('height', height + margin.top + margin.bottom) .append('g') .attr('transform', 'translate(' + margin.left + ',' + margin.top + ')'); // Create a skeleton structure for a tooltip and append it to the page const tip = d3 .select('body') .append('div') .attr('class', 'tooltip'); // Get the poll data from the /poll endpoint fetch('http://localhost:4000/poll') .then(response => response.json()) .then(poll => { // add the x Axis svg .append('g') .attr('transform', 'translate(0,' + height + ')') .attr('class', 'x-axis') .call(d3.axisBottom(x)); // add the y Axis svg .append('g') .attr('class', 'y-axis') .call(d3.axisLeft(y)); update(poll); }); function update(poll) { // Scale the range of the data in the x axis x.domain( poll.map(d => { return d.name; }) ); // Scale the range of the data in the y axis y.domain([ 0, d3.max(poll, d => { return d.votes + 200; }), ]); // Select all bars on the graph, take them out, and exit the previous data set. // Enter the new data and append the rectangles for each object in the poll array svg .selectAll('.bar') .remove() .exit() .data(poll) .enter() .append('rect') .attr('class', 'bar') .attr('x', d => { return x(d.name); }) .attr('width', x.bandwidth()) .attr('y', d => { return y(d.votes); }) .attr('height', d => { return height - y(d.votes); }) .on('mousemove', d => { tip .style('position', 'absolute') .style('left', ${d3.event.pageX + 10}px) .style('top', ${d3.event.pageY + 20}px) .style('display', 'inline-block') .style('opacity', '0.9') .html( <div><strong>${d.name}</strong></div> <span>${d.votes} votes</span> ); }) .on('mouseout', () => tip.style('display', 'none')); // update the x-axis svg.select('.x-axis').call(d3.axisBottom(x)); // update the y-axis svg.select('.y-axis').call(d3.axisLeft(y)); }
在上面的代码块中,我们使用通过/ poll端点接收的初始数据创建了一个基本条形图。如果您熟悉D3的工作原理,那么您应该熟悉这些代码。我在代码的关键部分添加了注释,以指导您构建图表的方式。
在新终端中,启动开发服务器以提供index.html文件:
npx http-server
我在这里使用http-server,但你可以使用你想要的任何服务器。您甚至可以直接在浏览器中打开index.html。
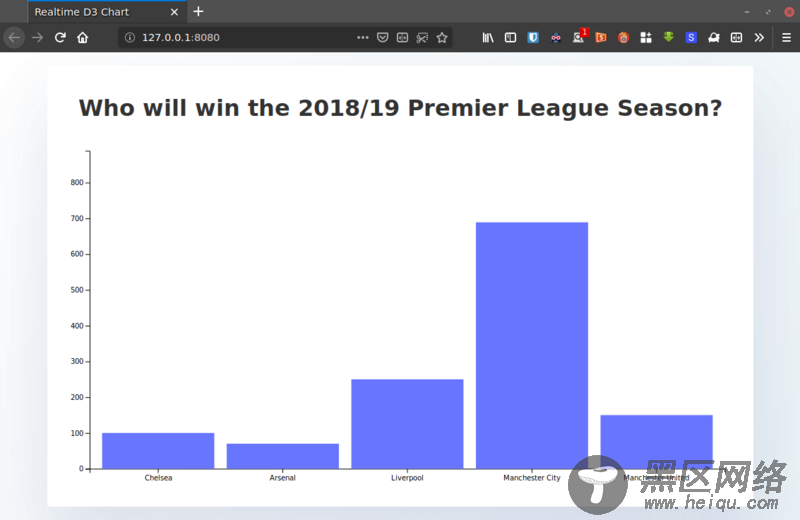
此时,您的图表应如下所示:
使用Pusher实时更新图表
让我们确保轮询的更新可以通过Pusher Channels实时反映在应用程序的前端中。将以下代码粘贴到app.js文件的末尾。
// app.js const pusher = new Pusher('<your app key>', { cluster: '<your app cluster>', encrypted: true, }); const channel = pusher.subscribe('poll-channel'); channel.bind('update-poll', data => { update(data.poll); });
在这里,我们打开了与Channels的连接,并使用Pusher的subscribe()方法订阅了一个名为poll-channel的新频道。通过bind方法监听轮询更新,并在收到更新后使用最新数据调用update()函数,以便重新呈现图形。
不要忘记使用Pusher帐户信息中心中的相应详细信息替换占位符。
从服务器触发更新
我们将模拟每秒更新一次的轮询,并在数据发生变化时使用Pusher触发更新,以便轮询的订阅者(客户端)可以实时接收更新的数据。
在其他导入下面的server.js顶部添加以下代码:
