文件锁是用于解决资源的共享使用的一种机制:当多个用户需要共享一个文件时,Linux 通常采用的方法是给文件上锁,来避免共享的资源产生竞争的状态。具体来讲,是通过借助 fcntl 函数来实现锁机制。当操作文件的进程没有获得锁时,虽然可以打开文件,但无法对文件执行执行 read、write 操作。
fcntl函数:
函数原型:
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
函数作用:
获取、设置文件访问控制属性。
参数介绍:
参数cmd有以下取值:
F_SETLK (struct flock *) 设置文件锁(trylock)
F_SETLKW (struct flock *) 设置文件锁(lock)W --> wait
F_GETLK (struct flock *) 获取文件锁
flock 结构体
struct flock
{
short l_type; /*F_RDLCK, F_WRLCK, or F_UNLCK*/
off_t l_start; /*相对于l_whence的偏移值,字节为单位*/
short l_whence; /*从哪里开始:SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR, or SEEK_END*/
off_t l_len; /*长度, 字节为单位; 0 意味着缩到文件结尾*/
pid_t l_pid; /*returned with F_GETLK*/
};
应用实例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/file.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int lock_set(int fd, int type)
{
struct flock old_lock, lock;
memset(&old_lock, 0, sizeof(old_lock));
memset(&lock, 0, sizeof(lock));
fcntl(fd, F_GETLK, &old_lock);
if(old_lock.l_type == F_WRLCK || old_lock.l_type == F_RDLCK)
{
if (old_lock.l_type == F_RDLCK)
printf("Read lock already set by %d \n", old_lock.l_pid);
else if (old_lock.l_type == F_WRLCK)
printf("Write lock already set by %d \n", old_lock.l_pid);
}
/* 配置 lock */
lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET;
lock.l_start = 0;
lock.l_len = 0;
lock.l_type = type;
lock.l_pid = -1;
lock.l_type = type;
if ((fcntl(fd,F_SETLKW,&lock)) < 0){
printf("Lock failed : type = %d \n",lock.l_type);
return 0;
}
switch(lock.l_type)
{
case F_RDLCK:
printf("Read lock set by %d \n", getpid());
break;
case F_WRLCK:
printf("write lock set by %d \n", getpid());
break;
case F_UNLCK:
printf("Release lock by %d \n", getpid());
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int fd;
fd = open("test",O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0644);
if(fd < 0){
printf("Open file error \n");
exit(1);
}
/* 写锁定 */
lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);
getchar();
/* 解锁 */
lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);
getchar();
close(fd);
return 0;
}
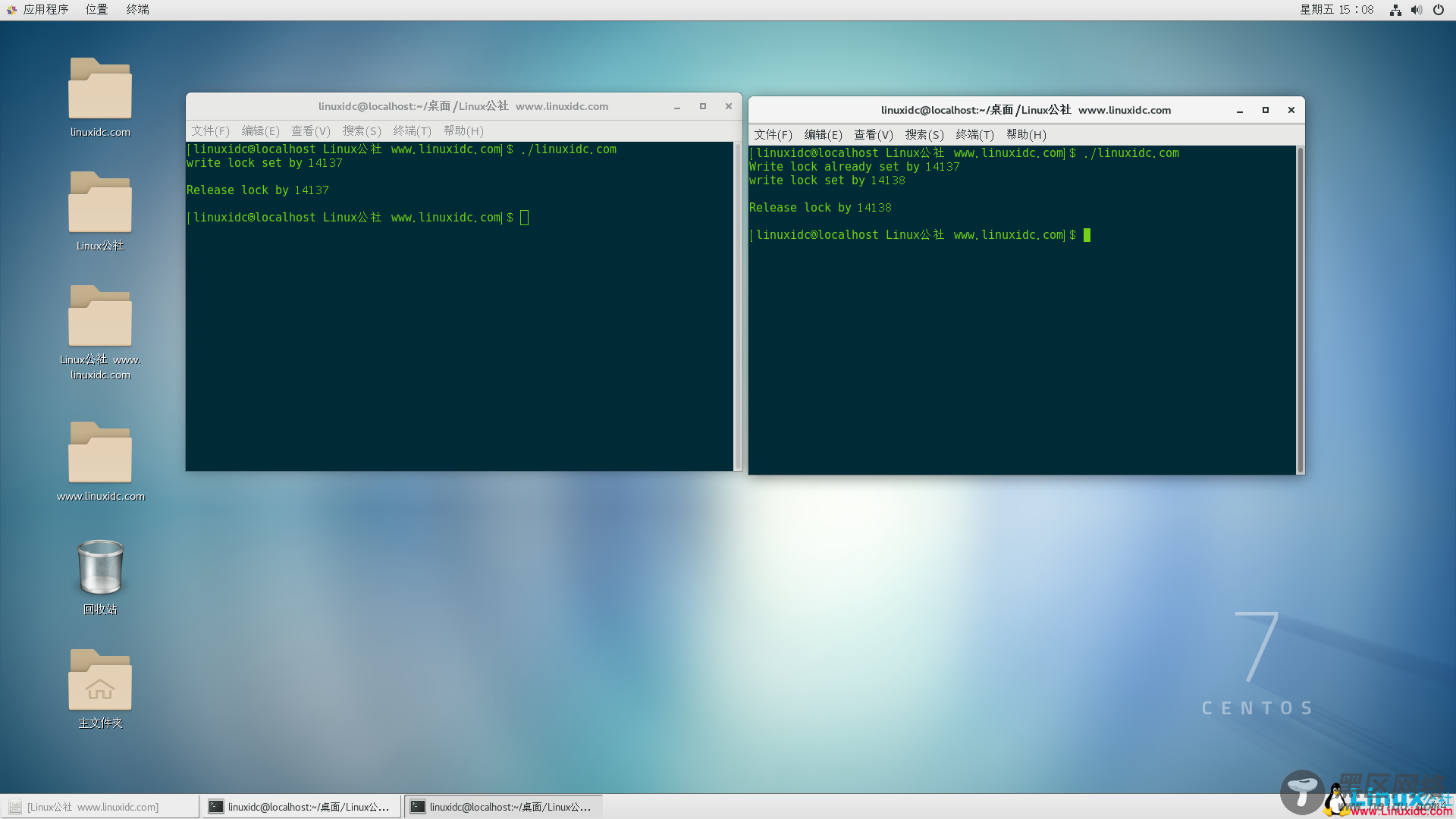
运行结果: