1.这部分框架类关系
2.Webwork 获取和包装 web 参数
3.DefaultActionProxyFactory、DefaultActionProxy、DefaultActionInvocation
一路走来,终于要开始 webwork 核心业务类的总结,webwork 通过对客户端传递的 web 参数重新包装,进行执行业务 Action 类,并反馈执行结果,本篇源码分析对应下图 WebWork 框架流转图中红色框的地方。
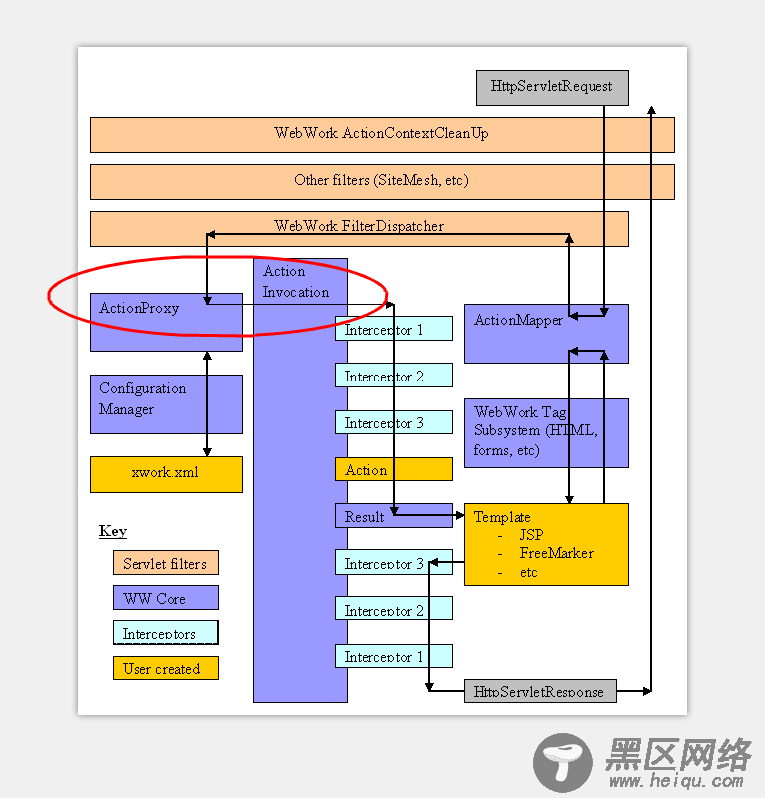
1.这部分框架类关系
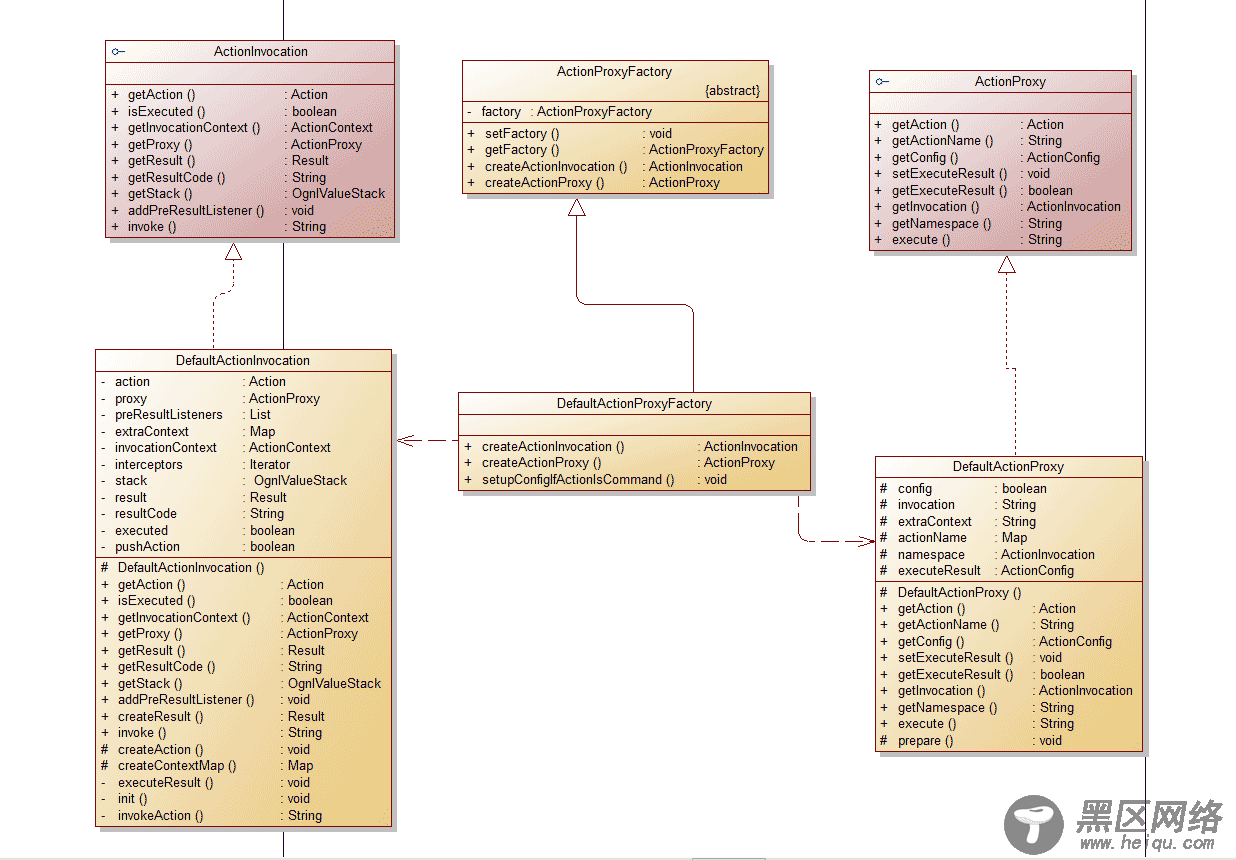
2.Webwork 获取和包装 web 参数
•每个Web 框架或多或少的对 Web 请求参数的包装,用来拿来方便自己使用,当然webwork 也不例外。
•Webwork 每次响应请求的入口方法:
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException { try { if (encoding != null) { try { request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding); } catch (Exception localException) { } } if (locale != null) { response.setLocale(locale); } if (this.paramsWorkaroundEnabled) { request.getParameter("foo"); } request = wrapRequest(request); //封装 request请求 serviceAction(request, response, getNameSpace(request), getActionName(request), getRequestMap(request), getParameterMap(request), getSessionMap(request), getApplicationMap()); } catch (IOException e) { String message = "Could not wrap servlet request with MultipartRequestWrapper!"; log.error(message, e); sendError(request, response, , new ServletException(message, e)); } }
•接受 request 、response 参数,并对 request 参数进行封装,这次封装主要是针对多媒体请求进行的特殊处理,例如项目中的文件上传请求,导出各种类型文件等...
•包装完 request 之后,service 方法调用 ServletDispatche.serviceAction() 方法,并调用 getApplicationMap、getSessionMap、getRequestMap、 getParameterMap、getActionName、getNameSpace 6 个方法开始了Action 业务逻辑调用前的前戏。
•getNameSpace 方法用来获得一个Action所属的名称空间,例如 : "/my/MyAction.action"则返回"/my",具体实现如下:
protected String getNameSpace(HttpServletRequest request){ String servletPath = request.getServletPath(); return getNamespaceFromServletPath(servletPath); } public static String getNamespaceFromServletPath(String servletPath){ servletPath = servletPath.substring(, servletPath.lastIndexOf("https://www.jb51.net/")); return servletPath; }
•getActionName 返回请求的Action的名字,例如:"MyAction.action"则返回"MyAction",具体实现如下:
protected String getActionName(HttpServletRequest request){ String servletPath = (String)request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.include.servlet_path"); if (servletPath == null) { servletPath = request.getServletPath(); } return getActionName(servletPath); } protected String getActionName(String name){ int beginIdx = name.lastIndexOf("https://www.jb51.net/"); int endIdx = name.lastIndexOf("."); return name.substring(beginIdx == - ? : beginIdx + , endIdx == - ? name.length() : endIdx); }
• getRequestMap 方法返回一个包含请求中所有属性的Map,具体实现类是 RequestMap,具体代码如下:
protected Map getRequestMap(HttpServletRequest request){
return new RequestMap(request);
}
•getParameterMap 方法返回一个包含请求中所有参数的Map,具体代码如下:
protected Map getParameterMap(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException{ return request.getParameterMap(); }
•getSessionMap 方法返回一个包含 session 中所有属性的 Map,具体实现类是 SessionMap,具体代码如下:
protected Map getSessionMap(HttpServletRequest request){ return new SessionMap(request); }
•getApplicationMap 方法返回一个包含 Application 中所有属性的Map,具体实现类 是ApplicationMap,具体代码如下:
protected Map getApplicationMap(){ return new ApplicationMap(getServletContext()); }
•WebWork之所以要把request 的属性、参数,session 中的属性,Application 中的属性封装成 Map,仅仅是为了自己使用方便。
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String namespace, String actionName, Map requestMap, Map parameterMap, Map sessionMap, Map applicationMap) { HashMap extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, parameterMap, sessionMap, applicationMap, request, response, getServletConfig()); extraContext.put("com.opensymphony.xwork.dispatcher.ServletDispatcher", this); OgnlValueStack stack = (OgnlValueStack) request.getAttribute("webwork.valueStack"); if (stack != null) { extraContext.put("com.opensymphony.xwork.util.OgnlValueStack.ValueStack", new OgnlValueStack(stack)); } try { ActionProxy proxy = ActionProxyFactory.getFactory().createActionProxy(namespace, actionName, extraContext); request.setAttribute("webwork.valueStack", proxy.getInvocation().getStack()); proxy.execute(); if (stack != null) { request.setAttribute("webwork.valueStack", stack); } } catch (ConfigurationException e) { log.error("Could not find action", e); sendError(request, response, 404, e); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Could not execute action", e); sendError(request, response, 500, e); } }
•首先 ServiceAction 调用了createContextMap 创建Action 上下文(extraContext)。 它将JavaServlet 相关的对象进行包装,放入extraContext Map对象里。
•接着检查 上一个请求中是否有可用的值堆栈,如果有就放入extraContext 这个Map 对象里,供本次请求使用 。
