arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,radius)
画曲线,要想明白它们之间的关系需要画辅助线
let x0 = 100, y0 = 100, x1 = 400, y1 = 100, x2 = 350, y2 = 150; ctx.beginPath(); ctx.moveTo(x0, y0); ctx.strokeStyle = "#f00"; ctx.lineWidth = 2; ctx.arcTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, 20); ctx.stroke(); ctx.beginPath(); ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(0,0,0,0.5)"; ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.moveTo(x0, y0); ctx.lineTo(x1, y1); ctx.fillText('x1,y1', x1 + 10, y1 + 10) ctx.lineTo(x2, y2); ctx.fillText('x2,y2', x2 + 10, y2) ctx.stroke();说明一下,x0,y0 起点坐标,x1,y1 第一个点坐标,x2,y2 第二个坐标
arcTo的规律: 他其实是通过起点,第1点,第2点的两条直线,组成了一个夹角,而这两条线,也是参数圆的切线。其中圆的半径决定了圆会在什么位置与线条发生切边。
让我们把球球变大吧!
ctx.arcTo(x1,y1,x2,y2,50); //半径改成50

我们发现他们还是相切的,因为切线可以无限延长
为了方便计算,我先把两条线的夹角改成90度。
var x0=100,
y0=400,
x1 = 500,
y1 = 400,
x2 = 500,
y2 = 450;
更改后就是90度张开了哟!我们保持球的半径不变。刷新后:
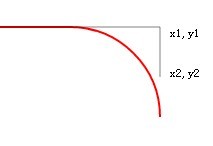
我们把y2变大,也就是延长了一条切线,把他变成550,刷新后:
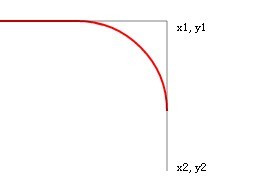
切线是延长了,但arcTo画出的红线没有任何变化。
写一个可行的案例吧
绘制一个背景网格
// 绘制网格 grid for (let x = 0.5; x < 500; x += 10) { ctx.moveTo(x, 0); ctx.lineTo(x, 500) } for (let y = 0; y < 500; y += 10) { ctx.moveTo(0, y) ctx.lineTo(500, y) } ctx.strokeStyle = '#eee'; ctx.stroke();
画两条直线相交
// lines ctx.strokeStyle = 'gray'; ctx.lineWidth = 1; ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(51, 24) ctx.lineTo(314, 540) ctx.moveTo(477, 34) ctx.lineTo(86, 484) ctx.stroke();
绘制两条线上的点
问题来了两点确定一条直线怎么知道线上的点的位置关系
两点式公式
(y-y2)/(y1-y2) = (x-x2)/(x1-x2)
求两条直线上面的交点
上demo代码
// 两点式公式 // (y-y2)/(y1-y2) = (x-x2)/(x1-x2)。 // 我们设y=200,可以求出x=140.7 ctx.beginPath() ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arc(140.7,200,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 设x=350,求右边直线的y点 180.16 ctx.moveTo(350,180.16) ctx.arc(350,180.16,5,0,2*Math.PI) // 求原点坐标 ctx.moveTo(211.713,339.3166) ctx.arc(211.713,339.3166,5,0,2*Math.PI) ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; ctx.fill();
标记点的位置
ctx.font='14px Arial' ctx.beginPath() ctx.fillText("(x0,y0)",140.7+5,200+5) ctx.fillText("(x1,y1)",350+5,180.16+5) ctx.fillText("(x2,y2)",211.713+5,339.3166+5)
画arcTo 曲线
// 编写arcTo ctx.beginPath() ctx.lineWidth=3; ctx.moveTo(140.7,200) ctx.arcTo(211.713,339.3166,350,180.16,100) ctx.stroke()
