或者,抽象一下:
public interface UserDAO {
void insertUser(UserDO userDO);
}
public class UserDAOImpl extends SqlMapDaoTemplate implements UserDAO {
public UserDAOImpl(DaoManager daoManager) {
super(daoManager);
}
public void insertUser(UserDO userDO) throws SQLException {
insert("insert", userDO);
}
}
两个实现,都涉及一个问题,需要手写
insert("insert", userDO);
那么写错,也是完全可能的嘛。但iBatis这部分,与Mybatis一样,是通过运行时的反射实现的。那么就无法快速失败,从而在启动时检索出问题。
如果一个不常用的方法实现的入参方法名写错了。Boom,线上故障+紧急发布。
所以,这里需要一个解决方案,可以在启动时,就检索出对应错误。
Mybatis给出的答案是,不再需要写上述实现。Mybatis直接通过Binding模块,直接关联DAO&对应Mapper。如果映射存在问题,则在启动时抛出相应问题。
举个栗子,如果在DAO的入参中没有String shopCode,而对应Mapper有对应入参注入,则会在启动时报错,提示“无法找到对应入参”。
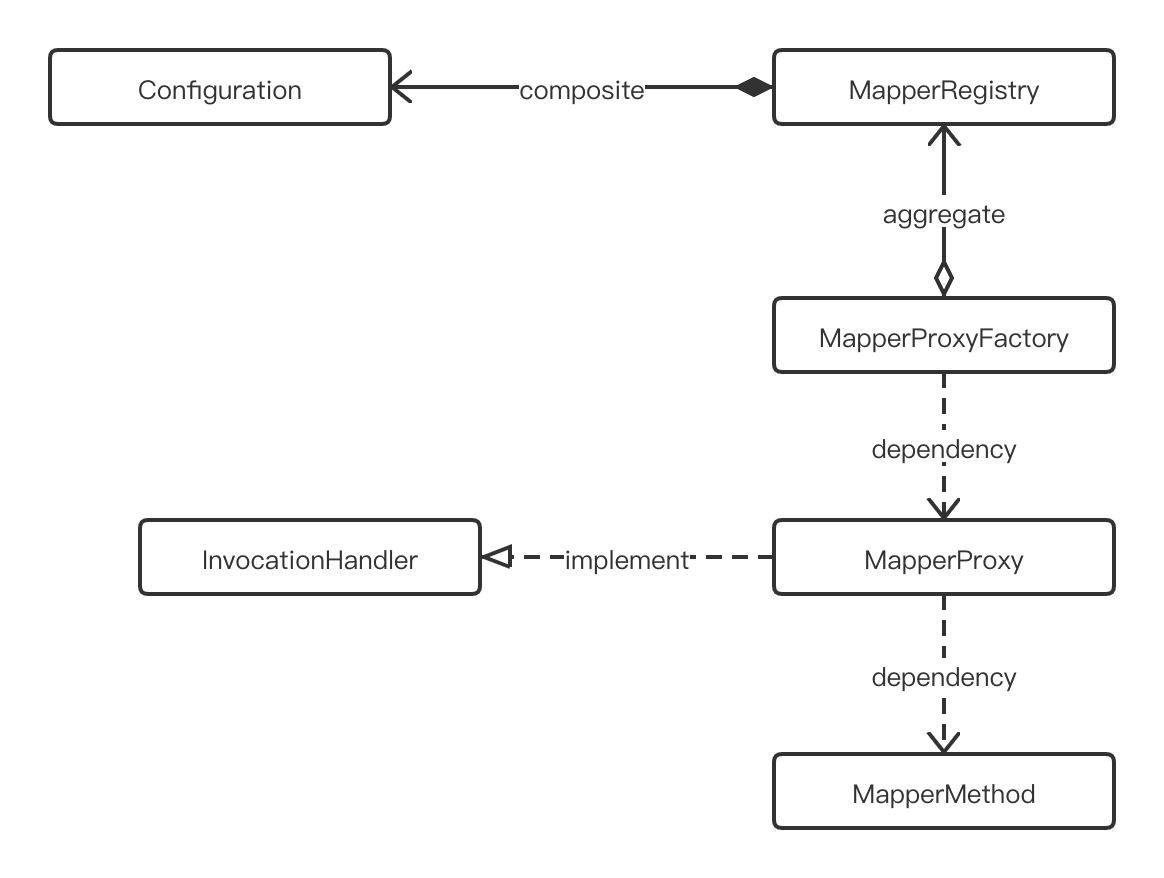
MapperRegistry
public class MapperRegistry {
// Mybatis全局Configuration,通过构造器注入
private final Configuration config;
// mapperInterface与相应MapperProxyFactory的映射表
// 如果是sqlSession.xxx的使用,则不经过这里。因为sqlSession在执行过程中,属于更底层的位置。详见后文:生命周期-执行过程
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
// 通过mapperInterface,获取对应的MapperProxy(type为接口类型)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
// 初始化过程中,用于添加mapperInterface。详见下述生命周期-初始化
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 检测type是否为接口类型,因为是针对mapperInterface
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 判断该接口是否已经注入到上面的映射表knownMappers中
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 进行对应mapper的解析,详见下述生命周期-初始化
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// 失败,“回滚”
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
// 其他方法
}
MapperProxyFactory
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 该接口中,method与对应Invoker的映射表。
// MapperMethodInvoker与MapperMethod关系,详见org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy.PlainMethodInvoker
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxy
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
// 核心字段
// 关联的SqlSession
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// 当前Mapper,所对应的mapperInterface
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 当前Mapper中,Method与Invoker对应的映射表,作为缓存。此是由MapperProxyFactory给出
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
// 核心方法
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如采目标方法继承自Object ,则直接调用目标方法。如toString()等方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 其他的方法,则是Mapper相关的方法(非Object方法),则需要通过MapperMethodInvoker。具体可参照下面的PlainMethodInvoker
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
MapperMethodInvoker invoker = methodCache.get(method);
if (invoker != null) {
return invoker;
}
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
// 默认方法是公共非抽象的实例方法。也就是Interface的default方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 根据默认方法的判定,常用的MapperMethodInvoker是PlainMethodInvoker
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
// 核心内部类
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 通过MapperMethod.execute(),进行Sql语句的代理执行。详见MapperMethod
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
}
MapperMethod


