洗牌算法题目
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Shuffle a set of numbers without duplicates.
*
* Example:
*
* // Init an array with set 1, 2, and 3. int[] nums = {1,2,3}; Solution
* solution = new Solution(nums);
*
* // Shuffle the array [1,2,3] and return its result. Any permutation of
* [1,2,3] must equally likely to be returned. solution.shuffle();
*
* // Resets the array back to its original configuration [1,2,3].
* solution.reset();
*
* // Returns the random shuffling of array [1,2,3]. solution.shuffle();
*
*/
public class Lc384 {
private int[] nums;
Random rand;
public Lc384(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
rand = new Random();
}
/** Resets the array to its original configuration and return it. */
public int[] reset() {
return nums;
}
/** Returns a random shuffling of the array. */
public int[] shuffle() {
int a[] = nums.clone();
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
int position = rand.nextInt(i + 1);
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[position];
a[position] = temp;
}
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Random random = new Random();
// while (true) {
// System.out.println(random.nextInt(2));
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// }
int[] nums = { 1, 2, 3 };
Lc384 lc384 = new Lc384(nums);
while (true) {
int[] arr = lc384.shuffle();
while (true) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
费雪耶兹算法
Fisher–Yates随机置乱算法也被称做高纳德置乱算法,通俗说就是生成一个有限集合的随机排列。Fisher-Yates随机置乱算法是无偏的,所以每个排列都是等可能的,当前使用的Fisher-Yates随机置乱算法是相当有效的,需要的时间正比于要随机置乱的数,不需要额为的存储空间开销。
一、算法流程:
需要随机置乱的n个元素的数组a:
for i 从n-1到1
j <—随机整数(0 =< j <= i)
交换a[i]和a[j]
end
二、实例
各列含义:范围、当前数组随机交换的位置、剩余没有被选择的数、已经随机排列的数
第一轮:从1到8中随机选择一个数,得到6,则交换当前数组中第8和第6个数
第二论:从1到7中随机选择一个数,得到2,则交换当前数组中第7和第2个数
下一个随机数从1到6中摇出,刚好是6,这意味着只需把当前线性表中的第6个数留在原位置,接着进行下一步;以此类推,直到整个排列完成。
截至目前,所有需要的置乱已经完成,所以最终的结果是:7 5 4 3 1 8 2 6
三、Java源代码
package simpleGa;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
<span class="hljs-keyword">public <span class="hljs-keyword">class <span class="hljs-title">Test {
<span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword">public <span class="hljs-keyword">static <span class="hljs-keyword">void <span class="hljs-title">main(<span class="hljs-params">String[] args) {
<span class="hljs-keyword">int[] arr = <span class="hljs-keyword">new <span class="hljs-keyword">int[<span class="hljs-number">10];
<span class="hljs-keyword">int i;
<span class="hljs-comment">//初始的有序数组
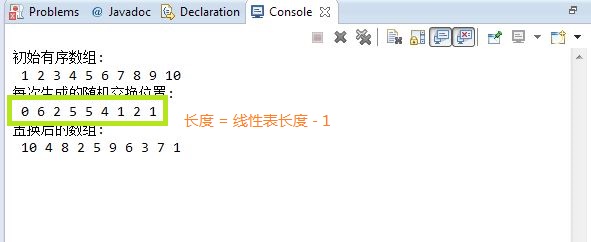
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.println(<span class="hljs-string">"初始有序数组:");
<span class="hljs-keyword">for (i = <span class="hljs-number">0; i < <span class="hljs-number">10; i++) {
arr[i] = i + <span class="hljs-number">1;
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.print(<span class="hljs-string">" " + arr[i]);
}
<span class="hljs-comment">//费雪耶兹置乱算法
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.println(<span class="hljs-string">"\n" + <span class="hljs-string">"每次生成的随机交换位置:");
<span class="hljs-keyword">for (i = arr.length - <span class="hljs-number">1; i > <span class="hljs-number">0; i--) {
<span class="hljs-comment">//随机数生成器,范围[0, i]
<span class="hljs-keyword">int rand = (<span class="hljs-keyword">new Random()).nextInt(i+<span class="hljs-number">1);
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.print(<span class="hljs-string">" " + rand);
<span class="hljs-keyword">int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[rand];
arr[rand] = temp;
}
<span class="hljs-comment">//置换之后的数组
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.println(<span class="hljs-string">"\n" + <span class="hljs-string">"置换后的数组:");
<span class="hljs-keyword">for (<span class="hljs-keyword">int k: arr)
System.<span class="hljs-keyword">out.print(<span class="hljs-string">" " + k);
}
}
分析:从运行结果可以看到随着算法的进行,可供选择的随机数范围在减小,与此同时此时数组里的元素更加趋于无序。
四、潜在的偏差