队列Queue这种数据结构,通常指先进先出(FIFO)这种容器。可以模拟生活中依次排队这种场景。
下面是集合体系继承树: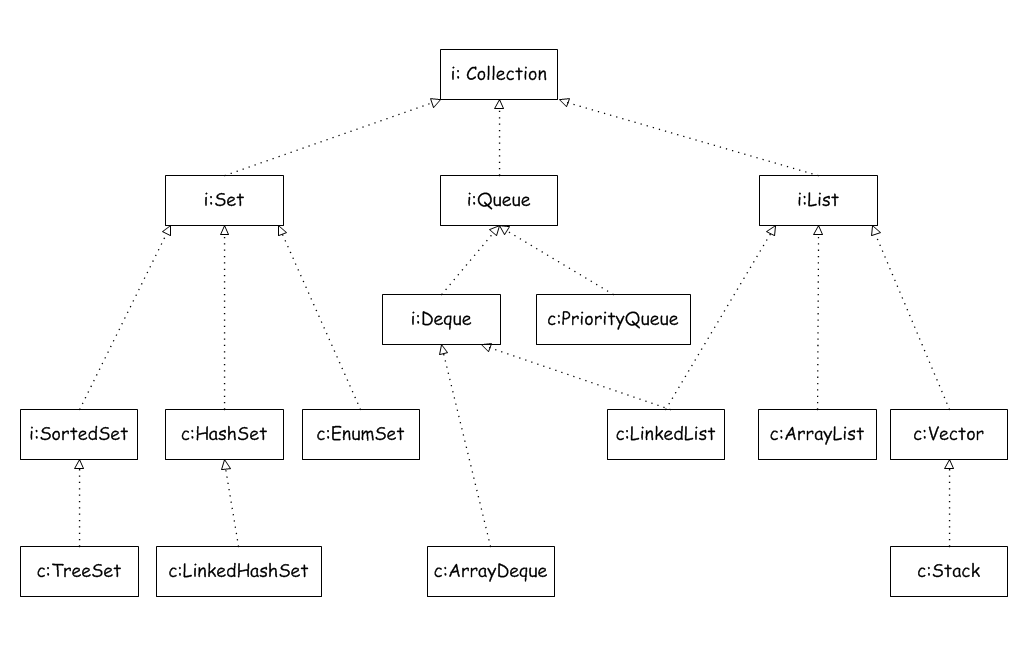
Queue和List一样都是Collection的子接口。
Queue源码定义: public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> { boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); E remove(); E poll(); E element(); E peek(); }add(E e)/offer(E e) 将指定元素加入到队列尾部
remove() 返回队列头部元素并删除,如果队列为空,会抛NoSuchElementException
poll() 返回队列头部元素并删除,如果队列为空,返回null
element() 返回队列头部元素不删除,如果队列为空,会抛NoSuchElementException
peek() 返回队列头部元素不删除,如果队列为空,返回null
Queue的实现有PriorityQueue、ArrayDeque、LinkedList。其中ArrayDeque、LinkedList是实现的其子接口Deque。
三、Deque从上面的继承图可以清楚的看到,Deque是Queue的子接口,它不仅是队列的数据结构,也是一个双端队列数据结构,同时也是一个栈(stack)的数据结构。
Deque源码定义: public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> { void addFirst(E e); void addLast(E e); boolean offerFirst(E e); boolean offerLast(E e); E removeFirst(); E removeLast(); E pollFirst(); E pollLast(); E getFirst(); E getLast(); E peekFirst(); E peekLast(); boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o); boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o); // *** Queue methods *** boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); E remove(); E poll(); E element(); E peek(); // *** Stack methods *** void push(E e); E pop(); // *** Collection methods *** boolean remove(Object o); boolean contains(Object o); public int size(); Iterator<E> iterator(); Iterator<E> descendingIterator(); }Deque的接口和上面的Queue的操作基本相同。xxxFirst操作队列头部元素,xxxLast操作队列尾部元素。
另外Deque可以表示一个栈(stack):具有后进先出(LIFO)的特征。
push(E e) 入栈
pop() 出栈,如果栈为空时出栈会抛出NoSuchElementException异常,所以在出栈之前先peek()查看头部元素,如果栈为空会返回null.
Stack类Java中还有一个Stack类,这个类继承Vector。
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {从源码中可以看到Stack的pop()和peek()方法都是被synchronized修饰的。因此Stack的栈是线程安全的,但也因此降低了栈的性能。所以当我们不需要线程安全的场景时,应该用Deque.
public synchronized E peek() public synchronized E pop()
