Android平台下的数据存储主要包括文件的流读取,轻量级数据库SQLite,ContentProvider和Preference
当App被安装后.其所在的安装包中会有一个相应的文件夹用于存放自己的数据.只有应用程序自己本身才对这个文件夹有写入权限,路径是/data/data/APP包名/.下面是使用文件I/O方法直接往手机中存储数据.主要使用了FileInputStream和FileOutputStream这个两个类.
更多Android源码下载
用户名与密码都是
具体下载目录在 /pub/Android源码集锦/
public class UIDataActivity extends Activity { public static final String ENCODING = "UTF-8"; String fileName="test.txt"; String message = "Android数据存储I/O例子 "; TextView textView; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); /* * 本示例是应用程序在私有数据文件夹下创建一个文件并读取其中的数据显示在TextView上 */ writeFileData(fileName,message); String result = readFileData(fileName); textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv); textView.setText(result); } public void writeFileData(String fileName,String message){ //使用FileOutputStream对象如果文件不存在或者不可以写入时.会抛出FileNotFoundException异常 try { FileOutputStream stream = openFileOutput(fileName, MODE_PRIVATE); byte[] bytes = message.getBytes(); stream.write(bytes); stream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } public String readFileData(String fileName){ String result =""; try { FileInputStream stream = openFileInput(fileName); int len = stream.available(); byte[] bytes = new byte[len]; stream.read(bytes); result = EncodingUtils.getString(bytes, ENCODING); stream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } }
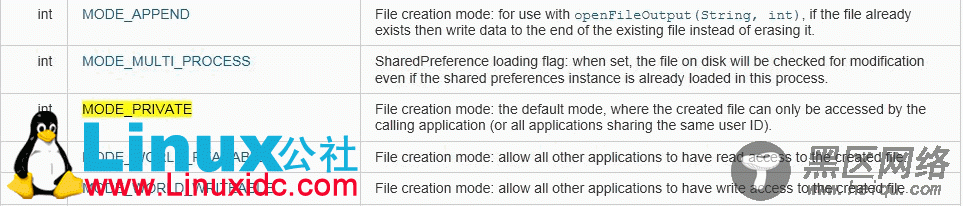
FileOutputStream第二个参数常数系统提供五种.