I/O线程池:组装好请求、送入I/O线程池等待执行,完成第一步I/O操作,进入第二部分回调通知。(在Windows中,线程池中的I/O操作调用完毕之后,会将获取的结果存在req->result属性上,然后调用PostQueuedCompletionStatus()通知IOCP,告知当前对象操作已经完成。)
异步I/O有如下图:
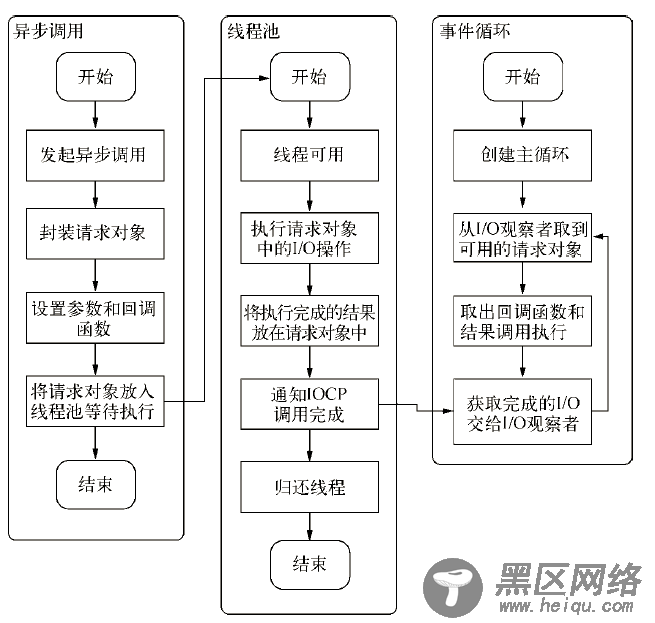
三.NodeJS异步编程实例:
前面介绍了异步I/O的相关概念,这里提供一个异步I/O操作的实例:
var config = require('./config.json'); var fs = require("fs"); var http = require('http'); var url_module = require("url"); http.createServer(function (request, response) { var key = url_module.parse(request.url).query.replace('key=', ''); switch (request.method) { case 'GET': // Asynchronous Response Generation fs.readFile(config.dataPath + key, 'utf8', function(err, value) { if (err) { // Return File Not Found if file hasn't yet been created response.writeHead(404, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'}); response.end("The file (" + config.dataPath + key + ") does not yet exist."); } else { // If the file exists, read it and return the sorted contents var sorted = value.split(config.sortSplitString).sort().join(''); response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'}); response.end(sorted); } }); break; case 'POST': // Synchronously append POSTed data to a file var postData = ''; request .on('data', function (data) { postData += data; }) .on('end', function () { fs.appendFile(config.dataPath + key, postData, function(err) { if (err) { // Return error if unable to create/append to the file response.writeHead(400, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'}); response.end('Error: Unable to write file: ' + err); } else { // Write or append posted data to a file, return "success" response response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'}); response.end('success'); } }); }); break; default: response.writeHead(400, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'}); response.end("Error: Bad HTTP method: " + request.method); } }).listen(config.serverPort); console.log('synchronous server is running: ', config.serverPort);
四.总结:
这篇博文是个人初次尝试NodeJS的一个小总结,如有写的不好还望大家多多的包含和指正。对于程序员来说,需要做的就是一直不停的学习,无论是否是自己主要从事的语言,对于学习多种语言,可以更加有助我们了解编程,对于一个开发者来说,最终的就是思想,因为语言的特性和框架的应用,一个熟练的编程者学习起来并不是难事,难就难在我们对于语言和框架的设计理念的理解。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
