The Garbage-First (G1) collector is a server-style garbage collector, targeted for multi-processor machines with large memories. It meets garbage collection (GC) pause time goals with a high probability, while achieving high throughput. The G1 garbage collector is fully supported in Oracle JDK 7 update 4 and later releases. The G1 collector is designed for applications that:
Can operate concurrently with applications threads like the CMS collector.
Compact free space without lengthy GC induced pause times.
Need more predictable GC pause durations.
Do not want to sacrifice a lot of throughput performance.
Do not require a much larger Java heap.
垃圾优先(G1)收集器是服务器样式的垃圾收集器,目标是具有大内存的多处理器计算机。 它极有可能满足垃圾回收(GC)暂停时间目标,同时实现高吞吐量。 * Oracle JDK 7更新4和更高版本中完全支持G1垃圾收集器*。 G1收集器设计用于以下应用程序:
可以与CMS收集器之类的应用程序线程并行运行。
紧凑的自由空间,无需较长的GC引起的暂停时间。
需要更多可预测的GC暂停时间。
不想牺牲很多吞吐量性能。
不需要更大的Java堆。
G1 is planned as the long term replacement for the Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector (CMS). Comparing G1 with CMS, there are differences that make G1 a better solution. One difference is that G1 is a compacting collector. G1 compacts sufficiently to completely avoid the use of fine-grained free lists for allocation, and instead relies on regions. This considerably simplifies parts of the collector, and mostly eliminates potential fragmentation issues. Also, G1 offers more predictable garbage collection pauses than the CMS collector, and allows users to specify desired pause targets.
G1计划作为并发标记扫描收集器(CMS)的长期替代产品。 将G1与CMS进行比较,有一些差异使G1成为更好的解决方案。 一个区别是G1是压紧收集器。 G1足够紧凑,可以完全避免使用细粒度的空闲列表进行分配,而是依赖于区域。 这大大简化了收集器的部分,并且大部分消除了潜在的碎片问题。 而且,G1提供的垃圾收集暂停比CMS收集器更具可预测性,并允许用户指定所需的暂停目标。
G1 Operational Overview
The older garbage collectors (serial, parallel, CMS) all structure the heap into three sections: young generation, old generation, and permanent generation of a fixed memory size
G1操作概述
较旧的垃圾收集器(串行,并行,CMS)将堆分为三个部分:固定内存大小的年轻代,旧代和永久代

All memory objects end up in one of these three sections.
The G1 collector takes a different approach.
所有内存对象最终都属于这三个部分之一。
G1收集器采用了不同的方法。
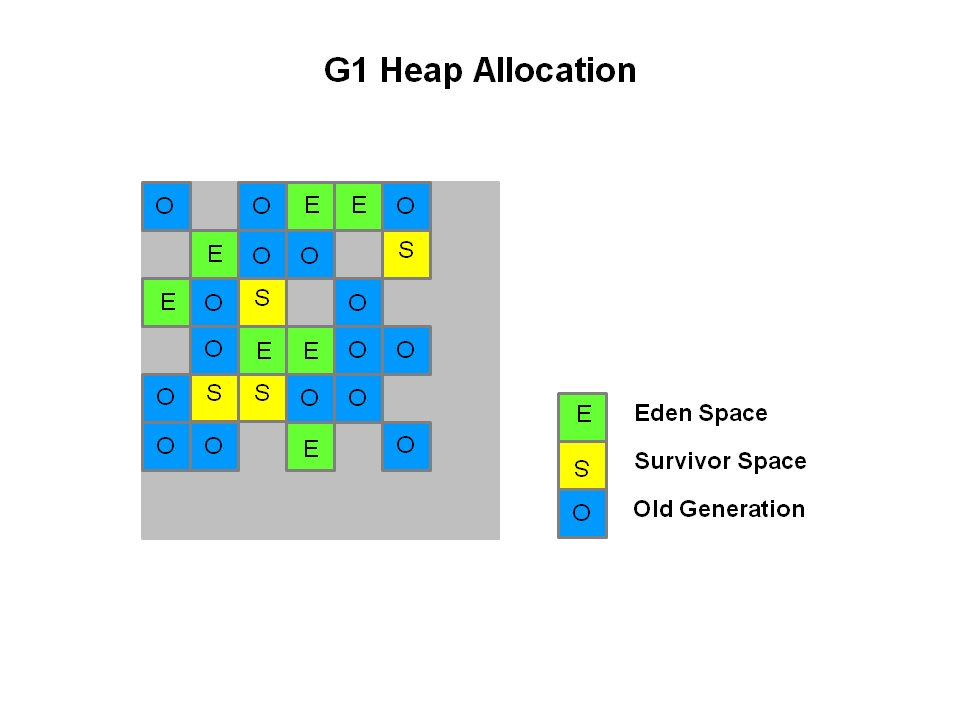
The heap is partitioned into a set of equal-sized heap regions, each a contiguous range of virtual memory. Certain region sets are assigned the same roles (eden, survivor, old) as in the older collectors, but there is not a fixed size for them. This provides greater flexibility in memory usage.
堆被划分为一组大小相等的堆区域,每个区域都有一个连续的虚拟内存范围。 某些区域集被分配了与较旧的收集者相同的角色(eden,幸存者,旧角色),但是它们的大小并没有固定。 这在内存使用方面提供了更大的灵活性。
When performing garbage collections, G1 operates in a manner similar to the CMS collector. G1 performs a concurrent global marking phase to determine the liveness of objects throughout the heap. After the mark phase completes, G1 knows which regions are mostly empty. It collects in these regions first, which usually yields a large amount of free space. This is why this method of garbage collection is called Garbage-First. As the name suggests, G1 concentrates its collection and compaction activity on the areas of the heap that are likely to be full of reclaimable objects, that is, garbage. G1 uses a pause prediction model to meet a user-defined pause time target and selects the number of regions to collect based on the specified pause time target.

