1. 什么是自动装配的歧义性?
在Spring中,装配bean有以下3种方式:
自动装配
Java配置
xml配置
在这3种方式中,自动装配为我们带来了很大的便利,大大的降低了我们需要手动装配bean的代码量。
不过,自动装配也不是万能的,因为仅有一个bean匹配条件时,Spring才能实现自动装配,如果出现不止1个bean匹配条件时,Spring就会不知道要装配哪个bean,抛出org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常,这就是自动装配的歧义性。
为了方便理解,我们举个具体的例子。
首先,我们新建个接口Dessert,该接口仅有1个方法showName():
package chapter03.ambiguity; public interface Dessert { void showName(); }然后定义3个该接口的实现类Cake,Cookies,IceCream:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Cake implements Dessert { @Override public void showName() { System.out.println("蛋糕"); } } package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Cookies implements Dessert { @Override public void showName() { System.out.println("饼干"); } } package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class IceCream implements Dessert { @Override public void showName() { System.out.println("冰激凌"); } }然后新建甜点店类DessertShop,该类的setDessert()方法需要装配1个Dessert的实例bean:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class DessertShop { private Dessert dessert; public Dessert getDessert() { return dessert; } @Autowired public void setDessert(Dessert dessert) { this.dessert = dessert; } public void showDessertName() { this.dessert.showName(); } }不过现在符合装配条件的有3个bean,它们的bean ID(默认情况下是类名首字母小写)分别为cake,cookies,iceCream,Spring该自动装配哪个呢?
带着这个疑问,我们先新建配置类AmbiguityConfig:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; @ComponentScan public class AmbiguityConfig { }这个类的关键是添加了@ComponentScan注解,让Spring自动扫描已经定义好的bean。
最后,新建类Main,在其main()方法中添加如下测试代码:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AmbiguityConfig.class); DessertShop dessertShop = context.getBean(DessertShop.class); dessertShop.showDessertName(); context.close(); } }运行代码,发现抛出org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常,如下所示:
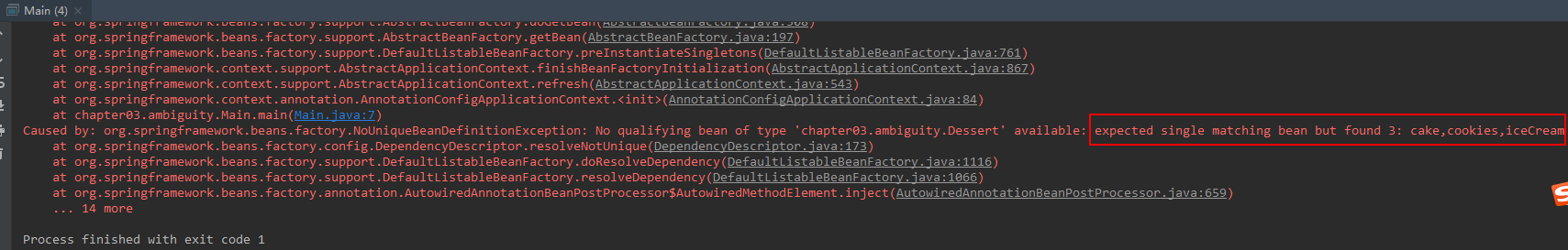
那么如何解决自动装配的歧义性呢?Spring提供了以下2种方案:
标记首选的bean
使用限定符
2. 标记首选的bean既然现在有3个匹配条件的bean,我们可以通过@Primary注解标记下哪个是首选的bean,这样当Spring发现有不止1个匹配条件的bean时,就会选择这个首选的bean。
比如3种甜点里,我最喜欢吃饼干,那么我就把Cookies标记为首选的bean:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Primary public class Cookies implements Dessert { @Override public void showName() { System.out.println("饼干"); } }再次运行测试代码,输出结果如下所示:
饼干
圆满解决了歧义性的问题,不过有一天,有个同事不小心在IceCream上也添加了@Primary注解:
package chapter03.ambiguity; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Primary public class IceCream implements Dessert { @Override public void showName() { System.out.println("冰激凌"); } }编译都正常,因此都没注意,但发布后运行时,却抛出如下异常:
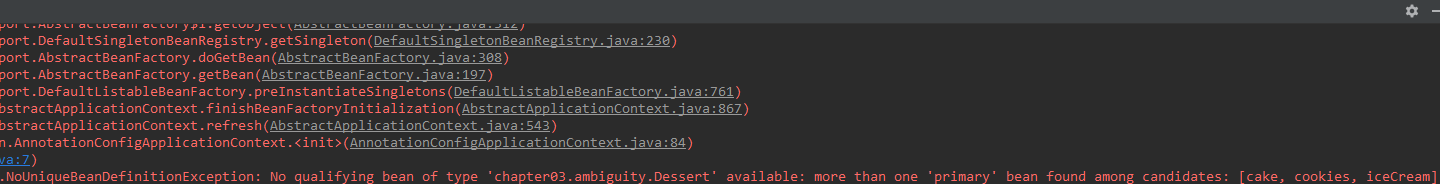
意思就是发现了不止1个首选的bean,因为此时Spring又不知道该选择哪个了,也就是有了新的歧义性,所以甩锅抛出了异常。
3. 使用限定符 3.1 基于bean ID的限定符Spring还提供了另一个注解@Qualifier注解来解决自动装配的歧义性,它可以与@Autowired或者@Inject一起使用,在注入的时候指定想要注入哪个bean。
比如,我们把IceCream注入到setDessert()的方法参数之中:
@Autowired @Qualifier("iceCream") public void setDessert(Dessert dessert) { this.dessert = dessert; }这里传递的iceCream指的是IceCream类默认生成的bean ID。
再次运行测试代码,输出结果如下所示:
冰激凌
我们可以发现,使用了@Qualifier注解后,我们之前标记的@Primary注解被忽略了,也就是说,@Qualifier注解的优先级比@Primary注解的优先级高。

