入栈时,新添加的元素位于队列的队尾,但是对于栈而言,它其实是栈顶元素。为了使得新添加的元素位于队首,可以将其之前的所有元素出队并重新入队。最终,队列中元素的顺序和出栈的顺序是一致的。具体的操作步骤如下图所示。
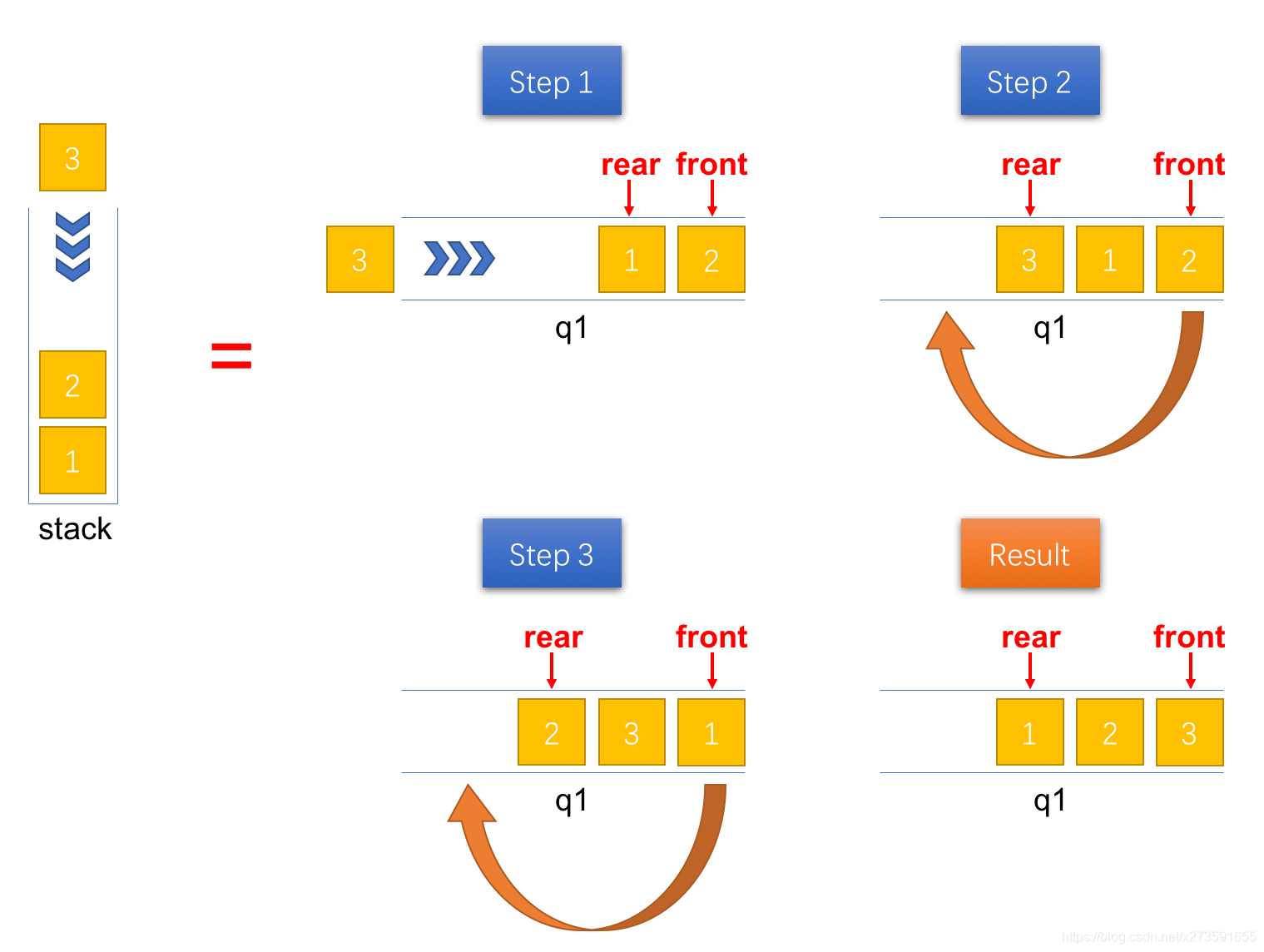
图5:将一个元素压入栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { queue.add(x); for (int i = 0; i < queue.size() - 1; ++i) { queue.add(queue.remove()); } }复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:\(O(n)\),其中 \(n\) 表示入栈前栈内元素的数目。入栈操作需要 \(n\) 次的出队操作,同时也需要 \(n + 1\)次的入队操作,因此,需要总的操作次数为 \(2n + 1\) 次。由于 LinkedList 的添加和删除操作的时间复杂度是 \(O(1)\) 的,因此,总的时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\)
空间复杂度:\(O(1)\)
出栈(pop)由于在入栈时已经将队列中的元素排列成出栈的顺序,因此,只需要出队队列 q1 中队首的元素即可。
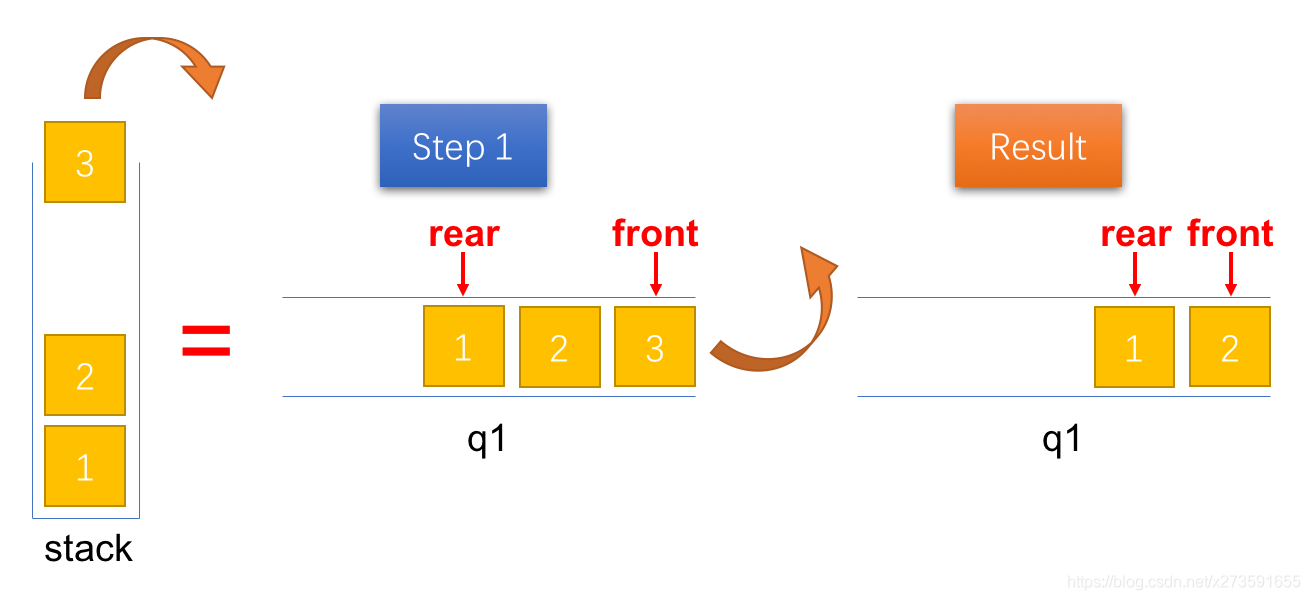
图6:将一个元素出栈
代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!"); } return queue.remove(); }复杂度分析如下:
时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
查看栈顶元素(peek)同理,只需要返回队列 q1 的队首元素即可。
/** Get the top element. */ public int top() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!"); } return queue.peek(); }复杂度分析如下:
时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
是否为空(empty)队列 q1 中保存了栈中的所有元素,因此,如果想要知道栈是否为空,只需要判断队列 q1 中是否还有元素,代码(Java)实现如下:
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return queue.isEmpty(); }复杂度分析如下:
时间复杂度:$ O(1) $
空间复杂度:$ O(1) $
Java 实现 import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; import java.util.Queue; class MyStack { private Queue<Integer> queue; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public MyStack() { queue = new LinkedList<>(); } /** Push element x onto stack. */ public void push(int x) { queue.add(x); for (int i = 0; i < queue.size() - 1; ++i) { queue.add(queue.remove()); } } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ public int pop() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!"); } return queue.remove(); } /** Get the top element. */ public int top() { if (queue.isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("[ERROR] The stack is empty!"); } return queue.peek(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ public boolean empty() { return queue.isEmpty(); } } /** * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack obj = new MyStack(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.top(); * boolean param_4 = obj.empty(); */ Python 实现 from collections import deque class MyStack: def __init__(self): """ Initialize your data structure here. """ self._q = deque() def push(self, x): """ Push element x onto stack. :type x: int :rtype: void """ self._q.append(x) for _ in range(len(self._q) - 1): self._q.append(self._q.popleft()) def pop(self): """ Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. :rtype: int """ if not self._q: raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!") return self._q.popleft() def top(self): """ Get the top element. :rtype: int """ if not self._q: raise Exception("[ERROR] The stack is empty!") return self._q[0] def empty(self): """ Returns whether the stack is empty. :rtype: bool """ return not self._q
