车道检测(Advanced Lane Finding Project)
实现步骤:
使用提供的一组棋盘格图片计算相机校正矩阵(camera calibration matrix)和失真系数(distortion coefficients).
校正图片
使用梯度阈值(gradient threshold),颜色阈值(color threshold)等处理图片得到清晰捕捉车道线的二进制图(binary image).
使用透视变换(perspective transform)得到二进制图(binary image)的鸟瞰图(birds-eye view).
检测属于车道线的像素并用它来测出车道边界.
计算车道曲率及车辆相对车道中央的位置.
处理图片展示车道区域,及车道的曲率和车辆位置.
Fork me on GitHub
相机校正(Camera Calibration)这里会使用opencv提供的方法通过棋盘格图片组计算相机校正矩阵(camera calibration matrix)和失真系数(distortion coefficients)。首先要得到棋盘格内角的世界坐标"object points"和对应图片坐标"image point"。假设棋盘格内角世界坐标的z轴为0,棋盘在(x,y)面上,则对于每张棋盘格图片组的图片而言,对应"object points"都是一样的。而通过使用openCv的cv::findChessboardCorners(),传入棋盘格的灰度(grayscale)图片和横纵内角点个数就可得到图片内角的"image point"。
void get_obj_img_points(const vector<string> & images,const cv::Size & grid,const cv::Size& distance,cv::Mat& cameraMatirx,cv::Mat& distCoeffs){ cv::Mat img,gray;//灰度图像 vector<cv::Point2f> corners;//用来储存t图片角点 vector<cv::Point3f> object_point;//保存标定板上所有角点坐标 vector<cv::Mat> rvecs,tvecs;//旋转向量和位移向量 vector<vector<cv::Point3f>> object_points;//棋盘格三维坐标容器 vector<vector<cv::Point2f>> img_points;//棋盘格角点容器 for(auto & imgdir:images){ //载入图像 img=cv::imread(imgdir); //生成object points for(int i=0;i<grid.height;i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid.width;j++){ object_point.push_back(cv::Point3f(i*distance.width,j*distance.height,0));//向容器存入每个角点坐标 } } //得到灰度图片 cv::cvtColor(img,gray,cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //得到图片的image points //NOTE corners的储存方式为从左往右,从上往下每行储存,所以储存object_point的时候需从grid。width开始遍历储存 bool ret=cv::findChessboardCorners(gray,grid,corners,cv::CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH+cv::CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE+cv::CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK); if(ret){//亚像素精细化 cv::cornerSubPix(gray,corners,cv::Size(11,11),cv::Size(-1,-1), cv::TermCriteria(cv::TermCriteria::COUNT+cv::TermCriteria::EPS, 30, 0.1)); img_points.push_back(corners); object_points.push_back(object_point); } object_point.clear();//清空object_point以便下一幅图使用该容器 //绘制角点并显示 cv::drawChessboardCorners(img,grid,cv::Mat(corners),ret); // cv::imshow("chessboard corners",img); // cv::waitKey(10); } cv::calibrateCamera(object_points,img_points,img.size(),cameraMatirx,distCoeffs,rvecs,tvecs); }然后使用上方法得到的object_points and img_points 传入cv::calibrateCamera() 方法中就可以计算出相机校正矩阵(camera calibration matrix)和失真系数(distortion coefficients),再使用 cv::undistort()方法就可得到校正图片。
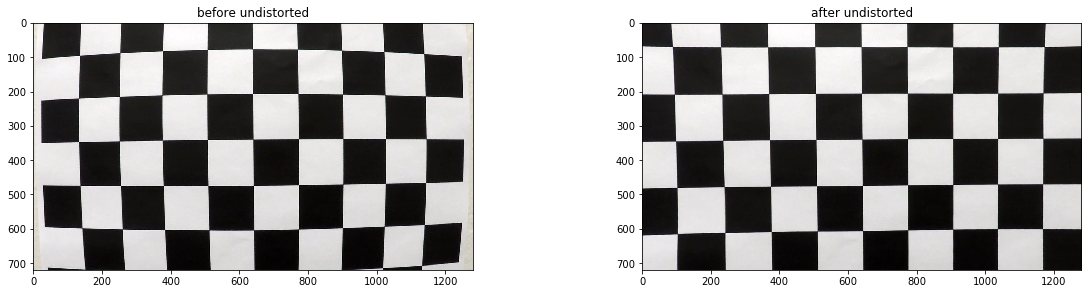
def cal_undistort(img, objpoints, imgpoints): ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, img.shape[1::-1], None, None) dst = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, mtx) return dst以下为其中一张棋盘格图片校正前后对比:
代码如下:
//获取棋盘格图片 get_images_by_dir(cal_dir,filetype,imgs); //计算矫正系数 get_obj_img_points(imgs,grid,distance,cameraMatirx,distCoeffs);测试图片校正前后对比:
[alt text][(https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RyanAdex/CarND-Advanced-Lane-Lines/master/output_images/undistortion.png)
这里会使用梯度阈值(gradient threshold),颜色阈值(color threshold)等来处理校正后的图片,捕获车道线所在位置的像素。(这里的梯度指的是颜色变化的梯度)
以下方法通过"cv::Sobel()"方法计算x轴方向或y轴方向的颜色变化梯度导数,并以此进行阈值过滤(thresholding),得到二进制图(binary image):
void abs_sobel_thresh(const cv::Mat& src,cv::Mat& dst,const char& orient='x',const int& thresh_min=0,const int& thresh_max=255){ cv::Mat src_gray,grad; cv::Mat abs_gray; //转换成为灰度图片 cv::cvtColor(src,src_gray,cv::COLOR_RGB2GRAY); //使用cv::Sobel()计算x方向或y方向的导 if(orient=='x'){ cv::Sobel(src_gray,grad,CV_64F,1,0); cv::convertScaleAbs(grad,abs_gray); } if(orient=='y'){ cv::Sobel(src_gray,grad,CV_64F,0,1); cv::convertScaleAbs(grad,abs_gray); } //二值化 cv::inRange(abs_gray,thresh_min,thresh_max,dst); // cv::threshold(abs_gray,dst,thresh_min,thresh_max,cv::THRESH_BINARY|cv::THRESH_OTSU); }通过测试发现使用x轴方向阈值在35到100区间过滤得出的二进制图可以捕捉较为清晰的车道线:
abs_sobel_thresh(imge,absm,'x',55,200);//sobel边缘识别
