本文是我关于Ocelot系列文章的第四篇,认证与授权。在前面的系列文章中,我们的下游服务接口都是公开的,没有经过任何的认证,只要知道接口的调用方法,任何人都可以随意调用,因此,很容易就造成信息泄露或者服务被攻击。
正如,我要找Willing干活之前,我得先到HR部门那里登记并且拿到属于我自己的工卡,然后我带着我的工卡去找Willing,亮出我是公司员工的身份,并且有权利要求他帮我完成一个任务。
在这里集成一套 .net core的服务认证框架IdentityServer4,以及如何在Ocelot中接入IdentityServer4的认证与授权。
跟上一篇Ocelot(三)- 服务发现文章中的Consul类似,这一个是关于Ocelot的系列文章,我暂时也不打算详细展开说明IdentityServer4,在本文中也是使用IdentityServer4最简单的Client认证模式。
关于更多的Ocelot功能介绍,可以查看我的系列文章
Ocelot - .Net Core开源网关
Ocelot(二)- 请求聚合与负载均衡
Ocelot(三)- 服务发现
本文中涉及案例的完整代码都可以从我的代码仓库进行下载。
仓库地址:https://gitee.com/Sevenm2/OcelotDemo
IdentityServer4使用IdentityServer4有多种认证模式,包括用户密码、客户端等等,我这里只需要实现IdentityServer4的验证过程即可,因此,我选择了使用最简单的客户端模式。
首先我们来看,当没有Ocelot网关时系统是如何使用IdentityServer4进行认证的。
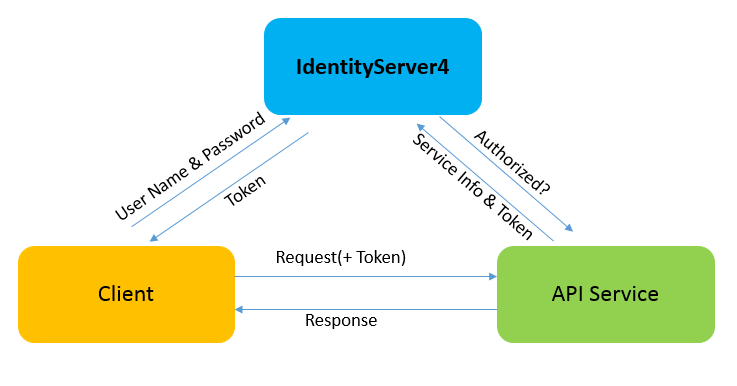
客户端需要先想IdentityServer请求认证,获得一个Token,然后再带着这个Token向下游服务发出请求。
我尝试根据流程图搭建出这样的认证服务。
创建IdentityServer服务端
新建一个空的Asp.Net Core Web API项目,因为这个项目只做IdentityServer服务端,因此,我将Controller也直接删除掉。
使用NuGet添加IdentityServer4,可以直接使用NuGet包管理器搜索IdentityServer4进行安装,或者通过VS中内置的PowerShell执行下面的命令行
Install-Package IdentityServer4
在appsettings.json中添加IdentityServer4的配置
{ "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } }, "SSOConfig": { "ApiResources": [ { "Name": "identityAPIService", "DisplayName": "identityAPIServiceName" } ], "Clients": [ { "ClientId": "mark", "ClientSecrets": [ "markjiang7m2" ], "AllowedGrantTypes": "ClientCredentials", "AllowedScopes": [ "identityAPIService" ] } ] }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }ApiResources为数组类型,表示IdentityServer管理的所有的下游服务列表
Name: 下游服务名称
DisplayName: 下游服务别名
Clients为数组类型,表示IdentityServer管理的所有的上游客户端列表
ClientId: 客户端ID
ClientSecrets: 客户端对应的密钥
AllowedGrantTypes: 该客户端支持的认证模式,目前支持如下:
Implicit
ImplicitAndClientCredentials
Code
CodeAndClientCredentials
Hybrid
HybridAndClientCredentials
ClientCredentials
ResourceOwnerPassword
ResourceOwnerPasswordAndClientCredentials
DeviceFlow
AllowedScopes: 该客户端支持访问的下游服务列表,必须是在ApiResources列表中登记的
新建一个类用于读取IdentityServer4的配置
using IdentityServer4.Models; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IdentityServer { public class SSOConfig { public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources(IConfigurationSection section) { List<ApiResource> resource = new List<ApiResource>(); if (section != null) { List<ApiConfig> configs = new List<ApiConfig>(); section.Bind("ApiResources", configs); foreach (var config in configs) { resource.Add(new ApiResource(config.Name, config.DisplayName)); } } return resource.ToArray(); } /// <summary> /// 定义受信任的客户端 Client /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients(IConfigurationSection section) { List<Client> clients = new List<Client>(); if (section != null) { List<ClientConfig> configs = new List<ClientConfig>(); section.Bind("Clients", configs); foreach (var config in configs) { Client client = new Client(); client.ClientId = config.ClientId; List<Secret> clientSecrets = new List<Secret>(); foreach (var secret in config.ClientSecrets) { clientSecrets.Add(new Secret(secret.Sha256())); } client.ClientSecrets = clientSecrets.ToArray(); GrantTypes grantTypes = new GrantTypes(); var allowedGrantTypes = grantTypes.GetType().GetProperty(config.AllowedGrantTypes); client.AllowedGrantTypes = allowedGrantTypes == null ? GrantTypes.ClientCredentials : (ICollection<string>)allowedGrantTypes.GetValue(grantTypes, null); client.AllowedScopes = config.AllowedScopes.ToArray(); clients.Add(client); } } return clients.ToArray(); } } public class ApiConfig { public string Name { get; set; } public string DisplayName { get; set; } } public class ClientConfig { public string ClientId { get; set; } public List<string> ClientSecrets { get; set; } public string AllowedGrantTypes { get; set; } public List<string> AllowedScopes { get; set; } } }
